Fig. 8.
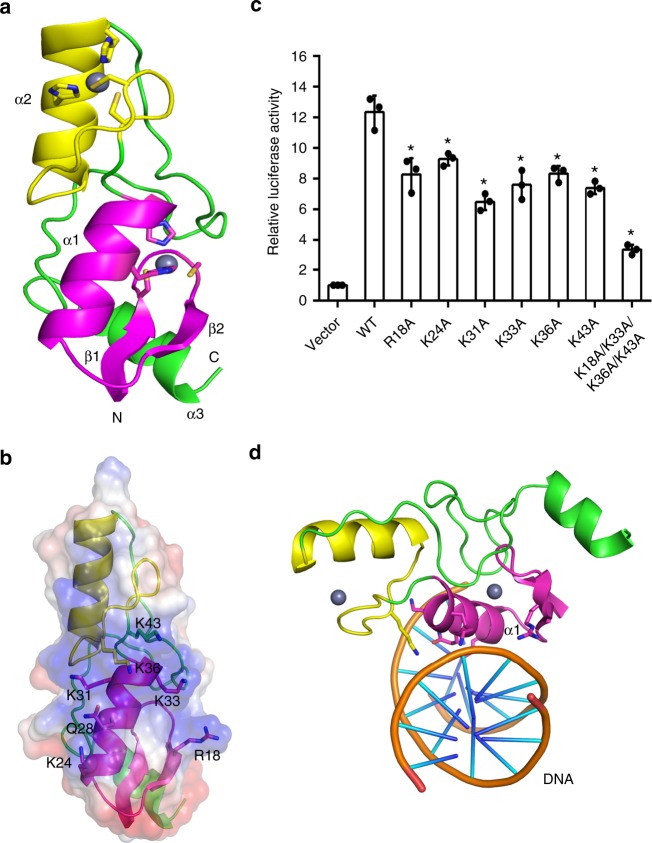
Identification of residues crucial to the function of OsSUF4. a Overall structure of OsSUF4. The first and second zinc finger domains are shown in magenta and yellow, respectively. Zinc ions are shown as gray spheres. b The detailed orientations of R18, K24, K31, K33, K36, and K43 within the first zinc finger domain of OsSUF4. c Dual luciferase assay showing Hd3a promoter activation by wild-type or mutated OsSUF4. Relative luciferase activity refers to normalization of firefly luciferase activity to the renilla luciferase activity as the internal control, then normalization to the vector (set as 1). Values are the mean ± SD of three independent biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences between WT and mutants (Student’s t-test: *P < 0.01). d The proposed OsSUF4–DNA-binding model. The first zinc finger domain of OsSUF4 is proposed to contact DNA via positively charged residues from the major groove side. Source data are provided as a Source Data file