Figure 1.
Generation of Specific Pathogenic Point Mutations in Human Tripronuclear Embryos Using the ABE System
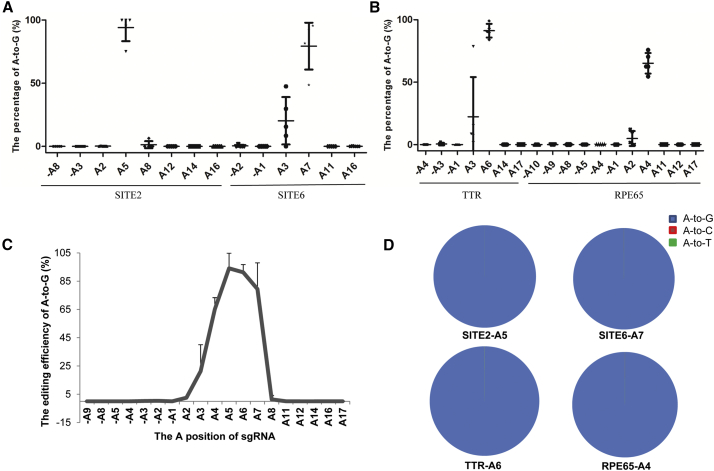
(A) Analysis of the ABE-mediated A-to-G editing of the reported sites in human embryos by deep sequencing. Two reported sites (SITE2 and SITE6) were selected to test the A-to-G editing in human tripronuclear embryos. The editing of all A sites 10 bp upstream of the sgRNA and within the sgRNA was analyzed by deep sequencing. Data of the detected embryos described in Table S1 are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 5). (B) Analysis of ABE-mediated A-to-G editing of the novel sites in human embryos by deep sequencing. Two novel sites, TTR and RPE65, were selected for A-to-G editing in human tripronuclear embryos. The editing of all the A sites 10 bp upstream and within the sgRNA was analyzed by deep sequencing. Data of the detected embryos described in Table S1 are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 5). (C) Characterization of the ABE-mediated A-to-G substitution at different positions in human tripronuclear embryos. (D) Analysis of different adenine substitutions of the target sites. The positions with most efficient editing of the 4 target sites were selected for analysis.