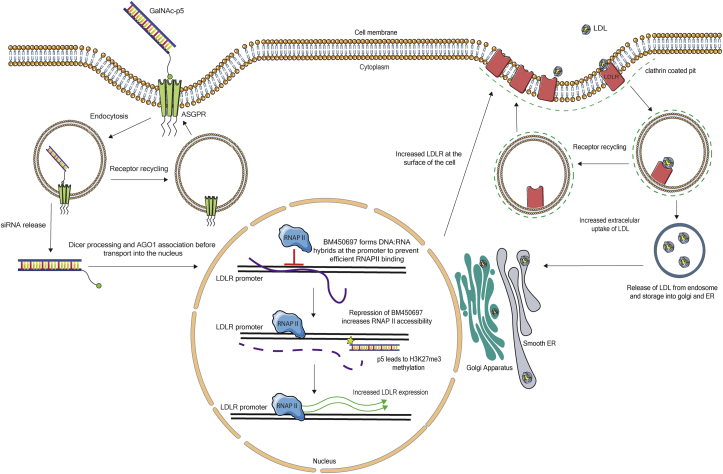
Figure 6.
Schematic Showing the Proposed Mechanism of BM450697 and the Proposed Effect of the Uptake of the siRNA-GalNAc Gal-p5 on BM450697 and LDLR Expression in the Cells
BM450697 expression results in a decrease in LDLR mRNA expression in hepatocytes by decreasing the accessibility of the Pol II binding site in the LDLR promoter. Upon GalNAc binding, the ASGPR is internalized into an endosome through endocytosis.31 Thereafter, the siRNA-GalNAc conjugate (Gal-p5) is processed and associates with AGO1.26 Once in the nucleus, the AGO1-associated complex exerts targeted gene silencing on BM450697, resulting in the loss of BM450697 through targeted TGS and H3k27me3 recruitment26 and an increase in LDLR mRNA expression. More LDLR protein is now processed and available in clathrin-coated pits located at the cell surface, allowing for an increase in LDL uptake and LDLR recycling to the surface of the cell.17, 20