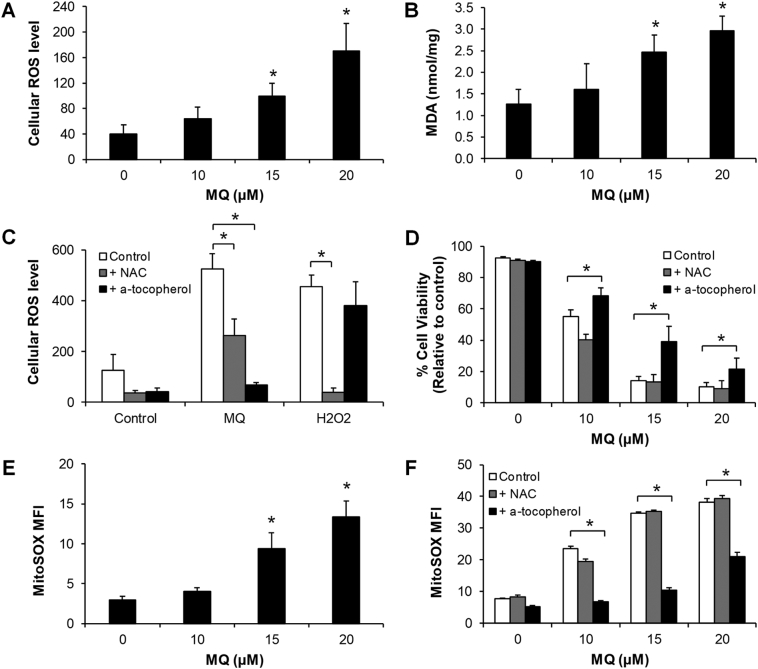
Figure 4.
Mefloquine induces oxidative stress and lysosomal lipid damage. (A) Mefloquine induces dose-dependent increase of intracellular ROS levels after 4 hours treatment in K562 cells. (B) Mefloquine induces dose-dependent increase of MDA levels in K562 cells after 24 hours treatment. α-tocopherol but not NAC significantly reversed the effects of mefloquine in increasing ROS levels (C) and decreasing viability (D) in K562 cells after 24 hours. On the other hand, ROS generated by H2O2 (50 μM) could be rescued by NAC but not α-tocopherol (C). (E) Mefloquine increases MitoSOX levels in K562 cells after 24 hours treatment. (F) α-tocopherol but not NAC significantly reversed the effects of mefloquine in increasing MitoSOX levels in K562 cells after 24 hours. Antioxidants α-tocopherol and NAC were used at 10 mM. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. All error bars as shown are standard deviation. *, P ≪ .05, compared to control.