Table 2.
GRADE assessment of the outcomes
| Certainty assessment | № of patients | Effect | Certainty | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Zn | Placebo | Absolute (95% CI) | |
| Number connection test | ||||||||||
| 3 | randomized trials | seriousa | not serious | not serious | not serious | publication bias strongly suspected strong associationb | 116 | 111 | SMD 0.97 lower (1.75 lower to 0.19 lower) |
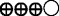 MODERATE MODERATE |
| Digital symbol test | ||||||||||
| 2 | randomized trials | seriousa | not serious | not serious | seriousc | publication bias strongly suspected strong associationb | 70 | 67 | SMD 0.44 higher (0.12 lower to 1 higher) |
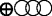 VERY LOW VERY LOW |
| Serum ammonia lev | ||||||||||
| 2 | randomized trials | seriousa | not serious | not serious | seriousc | publication bias strongly suspected strong associationb | 70 | 67 | MD 10.86 lower (25.73 lower to 4.01 higher) |
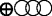 VERY LOW VERY LOW |
CI Confidence interval, SMD Standardized mean difference, MD Mean difference
Explanations
aWe downgraded by one level for serious risk of bias: one study was unblinded
bPublication bias was not assessed due to the limited numbers of included trials
cWe downgraded by one level for serious imprecision: the wide confidence interval contains significant benefits and harm
