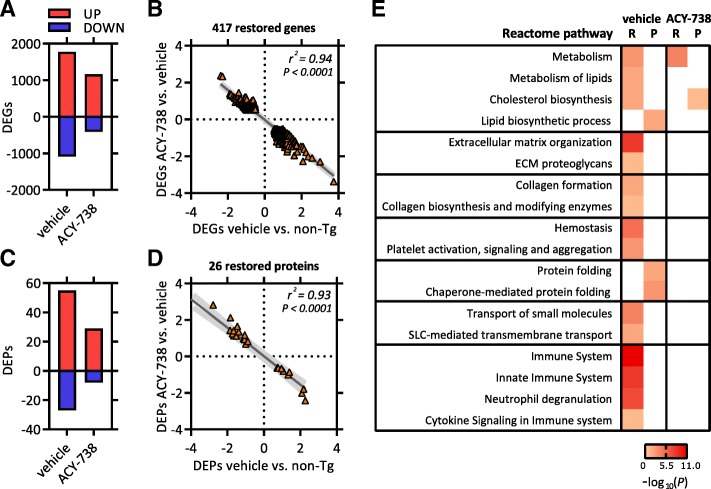
Fig. 7.
HDAC inhibition using ACY-738 restores transcriptional and proteomic alterations in spinal cord of Tg FUS+/+ mice. a Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in vehicle- or ACY-738-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice compared to non-Tg controls. b Pearson correlation analysis on genes with completely restored expression after ACY-738 therapy. Correlation between expression values in vehicle-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice compared to non-Tg controls (x-axis) versus the expression values in ACY-738-treated compared to vehicle-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice (y-axis). c Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in vehicle- or ACY-738-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice compared to non-Tg controls. d Pearson correlation analysis on proteins with completely restored expression after ACY-738 therapy. Correlation between expression values in vehicle-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice compared to non-Tg controls (x-axis) versus the expression values in ACY-738-treated compared to vehicle-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice (y-axis). e Heatmap of –log10 P-values of pathways that were significantly enriched after panther gene ontology (GO) analysis on differentially expressed genes/proteins in vehicle-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice compared to non-Tg controls, and in ACY-738-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice compared to vehicle-treated Tg FUS+/+ mice. RNA sequencing (R), proteomics (P)