Figure 2-.
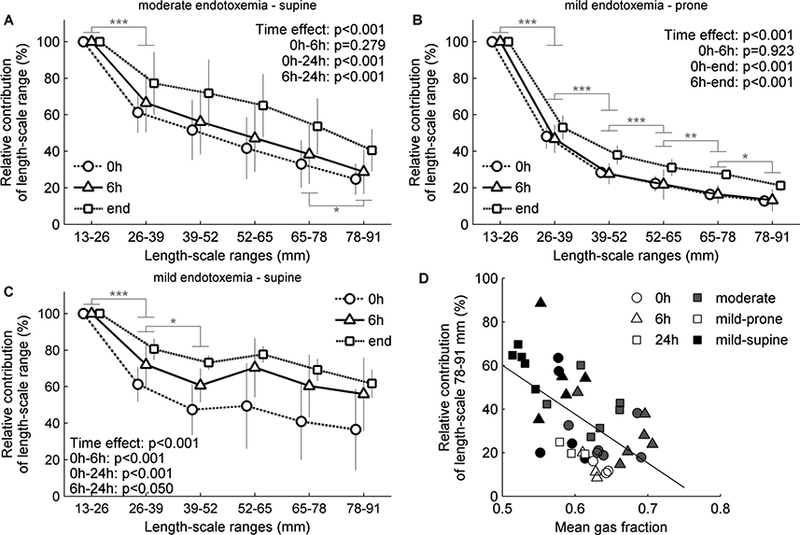
Contribution of length-scale ranges to lung aeration heterogeneity. Sheep with moderate (A, 10 ng/kg/min LPS) or mild (B-C, 2.5 ng/kg/min LPS) endotoxemia were mechanically ventilated using low tidal volume and low to moderate positive end- expiratory pressure. The contribution of a length-scale range was assessed by the difference between the variances normalized by the square mean in mean lung volume images filtered for effective resolutions from 13 to 91 mm. Values were expressed relative to the smallest length-scale (13–26 mm). In both endotoxemia levels and body positions (supine, A and C, prone, B), the largest contribution to heterogeneity was in the length-scale 13–26 mm, with an increase in the contribution of larger length-scales along time. Contribution of larger length-scales decreased with the mean gas fraction (D).* p<0.05, ** p<0.01 and *** p<0.001 for differences between consecutive length-scales.
