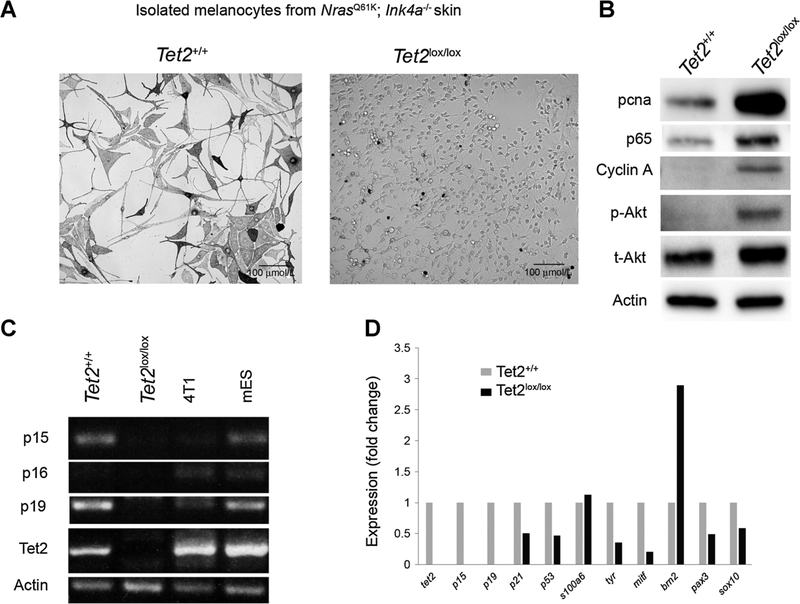
Figure 4.
Isolated Tet2+/+ and Tet2lox/lox melanocytes show different morphologies and abilities to grow in vitro. A, Picture showing the gross morphology of melanocytes isolated from Tet2+/+ and Tet2lox/lox mice sharing the Tyr::NrasQ61K; Tyr::Cre; Ink4a−/− background, n = 1 for each genotype. B, Western blot analysis of isolated and cultured melanocytes shows enhanced levels of proliferation-related proteins (Pcna and cyclin A) and Akt-pathway proteins, specifically in Tet2lox/lox cells. C, RT-PCR–based analysis of gene expression of four cell types. Unrelated cell types as controls: the 4T1 murine breast cancer cell line and mouse embryonic stem cells (mESC). Expression of cell-cycle inhibitor genes is lost in Tet2lox/lox cells as compared with Tet2+/+ cells. D, qRT-PCR analysis of cell-cycle gene and melanocyte marker gene expression.