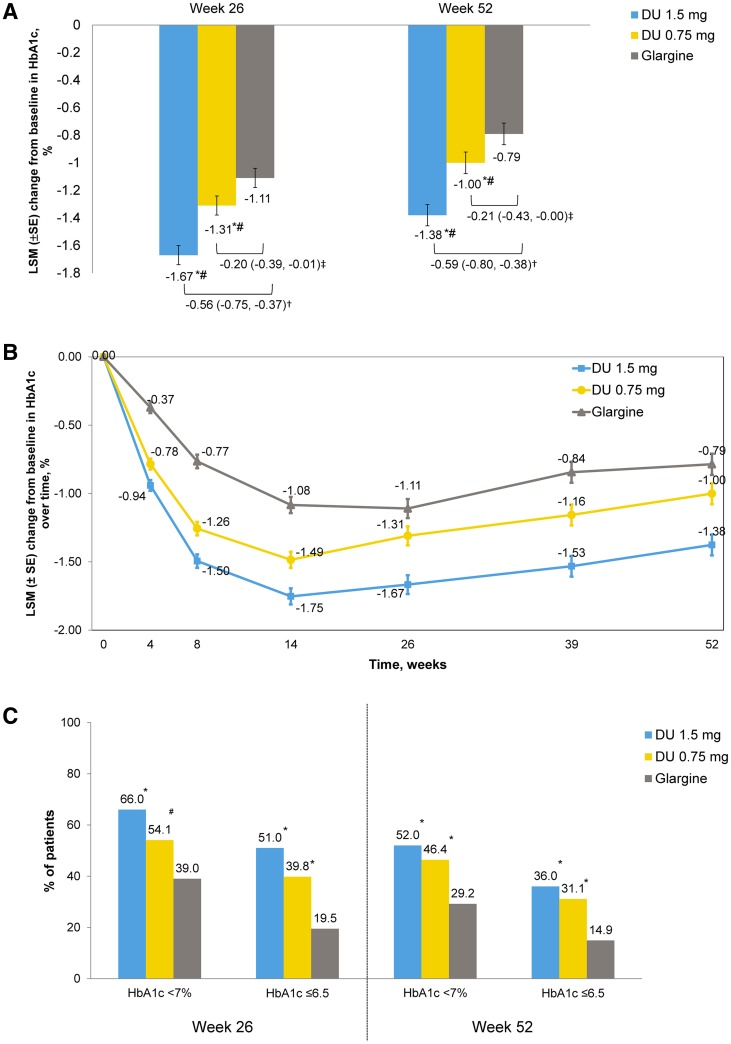
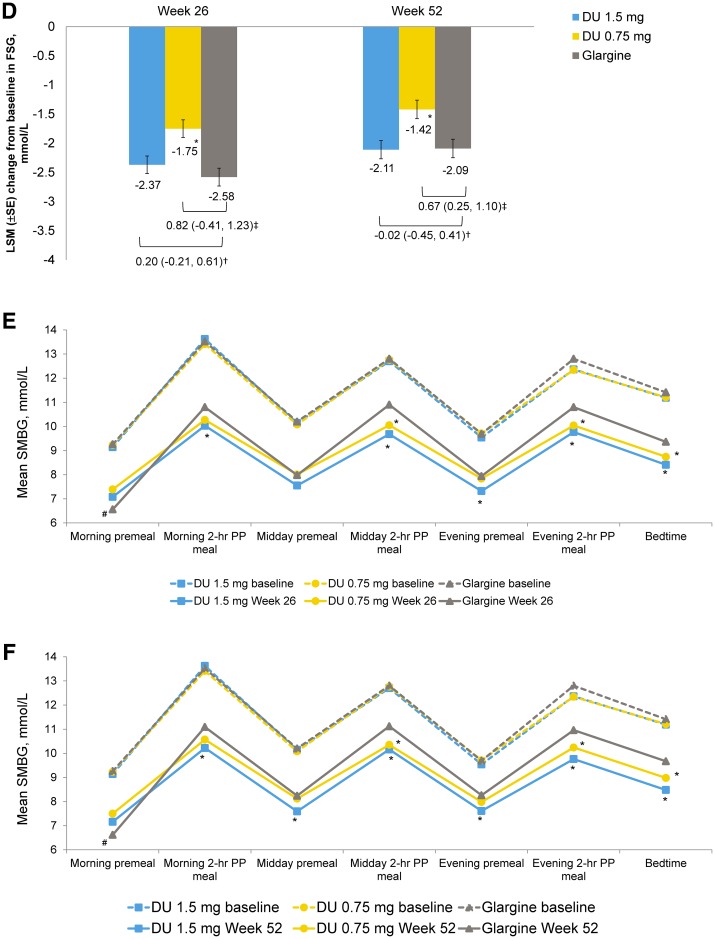
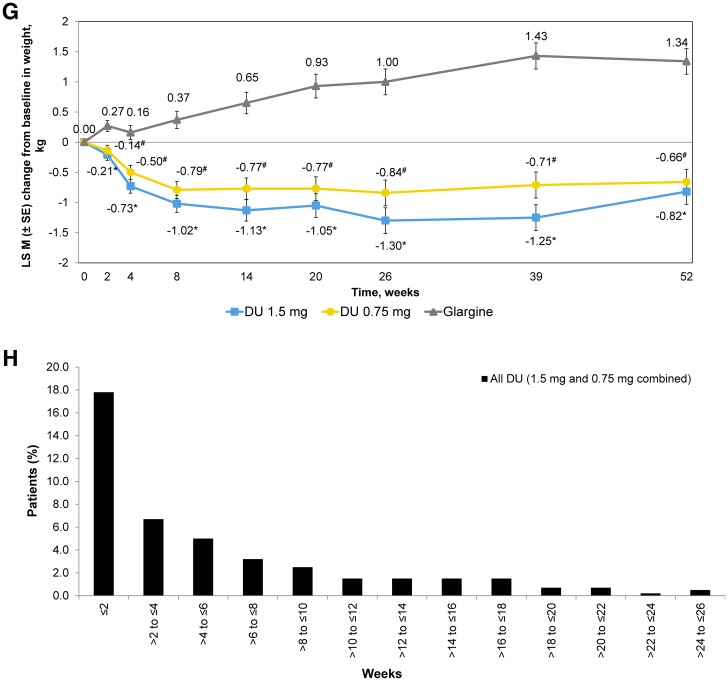
Fig. 3.
Efficacy and safety outcome measures. a LSM (SE) change in HbA1c (%) from baseline to 26 weeks and to 52 weeks. †LSM difference (95% CI) of dulaglutide 1.5 mg with glargine. ‡LSM difference (95% CI) of dulaglutide 0.75 mg with glargine. *Dulaglutide noninferior to glargine (two-sided P value < 0.001). #Dulaglutide superior to glargine (two-sided P value < 0.05). CI confidence interval, DU dulaglutide, HbA1c glycated hemoglobin, LSM least squares mean, SE standard error. b LSM (SE) change in HbA1c (%) from baseline over time. c Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c targets at week 26 and at week 52. *P < 0.001 dulaglutide vs glargine. #P < 0.05 dulaglutide vs glargine. d LSM (SE) change in fasting serum glucose (mmol/L) from baseline to week 26 and to week 52. †LSM difference (95% CI) of dulaglutide 1.5 mg with glargine. ‡LSM difference (95% CI) of dulaglutide 0.75 mg with glargine. *P < 0.05 dulaglutide vs glargine. FSG fasting serum glucose. 7-point self-monitored blood glucose profiles (mmol/L) by time of day at the end of e week 26 and f week 52. *P < 0.05 dulaglutide vs glargine. #P < 0.05 glargine vs dulaglutide. hr hour, PP postprandial, SMBG self-monitored blood glucose. g LSM (SE) change in body weight (kg) from baseline to 52 weeks. *P < 0.001 dulaglutide 1.5 mg vs glargine. #P < 0.001 dulaglutide 0.75 mg vs glargine. h Summary of occurrence of gastrointestinal treatment-emergent adverse events