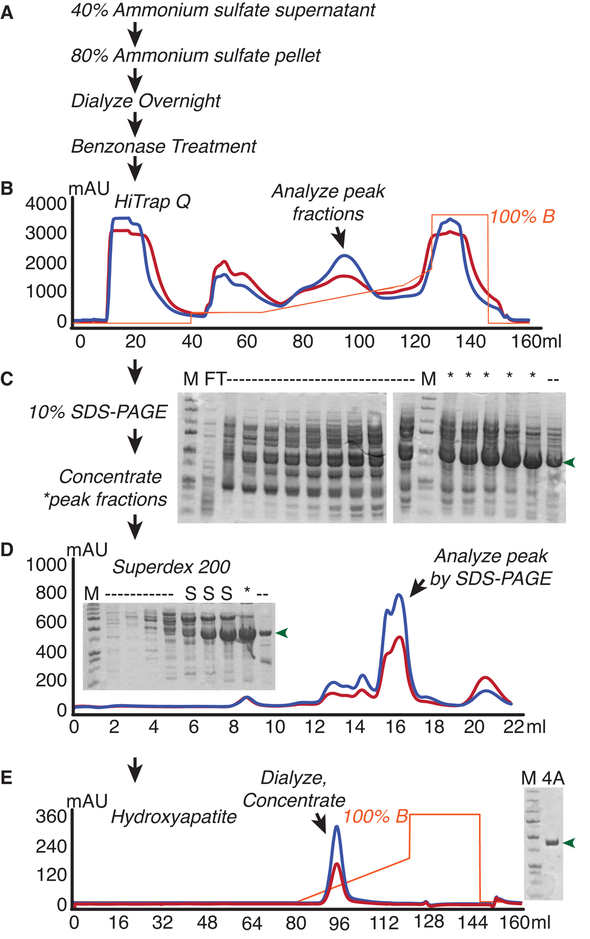
Figure 2.
Yeast eIF4A purification from E.coli. E.coli overexpressing yeast eIF4A were lysed and subjected to (A) Ammonium sulfate fractionation followed by Benzonase nuclease treatment to remove nucleic acids. eIF4A was then purified from lysates by B) Anion Exchange chromatography, D) Size Exclusion Chromatography, and E) Hydroxyapatite chromatography. Flowthrough (FT) and peak fractions were analyzed alongside marker (M) after each chromatographic step to monitor purity. Lanes with discarded fractions are noted as dashes, whereas desirable eIF4A fractions that were retained are denoted with asterisks, and shoulder fractions from the superdex column are denoted as “S”. eIF4A is indicated with green arrows.