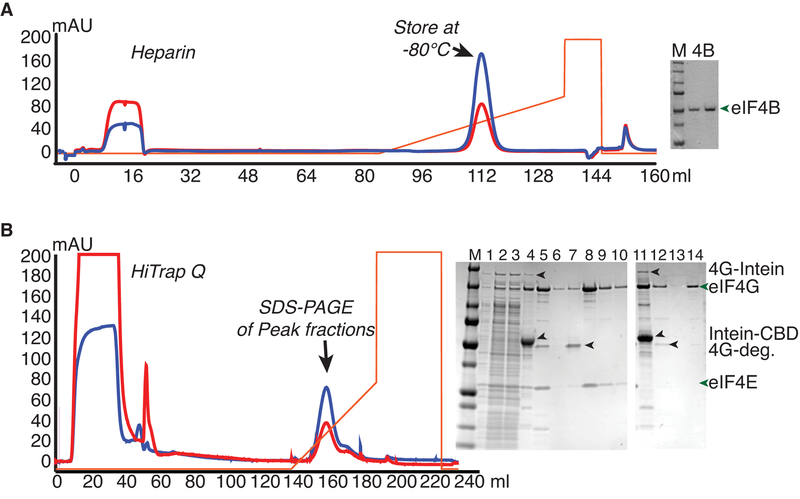
Figure 3.
Purification of Intein-Fusions of yeast eIF4B and eIF4G from E.coli. A. eIF4B was expressed as an intein-chitin-binding domain (CBD) fusion protein, and purified by running over a chitin column and eluting by intein cleavage with DTT buffer. Chromatogram shows eluate fractionation over a Heparin column. Gel shows Precision plus marker (M; Biorad) next to two dilutions of purified eIF4B. B. eIF4G fused to the intein-CBD was purified by binding to and washing on chitin resin followed by on-column nuclease digestion with micrococcal nuclease. Further washing was followed by DTT-induced intein-cleavage to elute eIF4G (complexed with eIF4E or without eIF4E). Chromatogram of anion exchange (Q) chromatography of eIF4G•eIF4E chitin eluate, from which full-length eIF4G eluted after degradation products. SDS-PAGE analysis shows separation of eIF4G•eIF4E (1–10) or eIF4G (11–13) from contaminants, with following loading order: M - Marker, 1) Lysate, 2–3) Low Speed supernatant, 4) Chitin Beads, 5) Q load, 6) Q flowthrough, 7–10) fractions from peaks 1 and 2, 11) Chitin Beads, 12) Q load, 13) Q flowthrough, and 14) major eIF4G peak fraction.