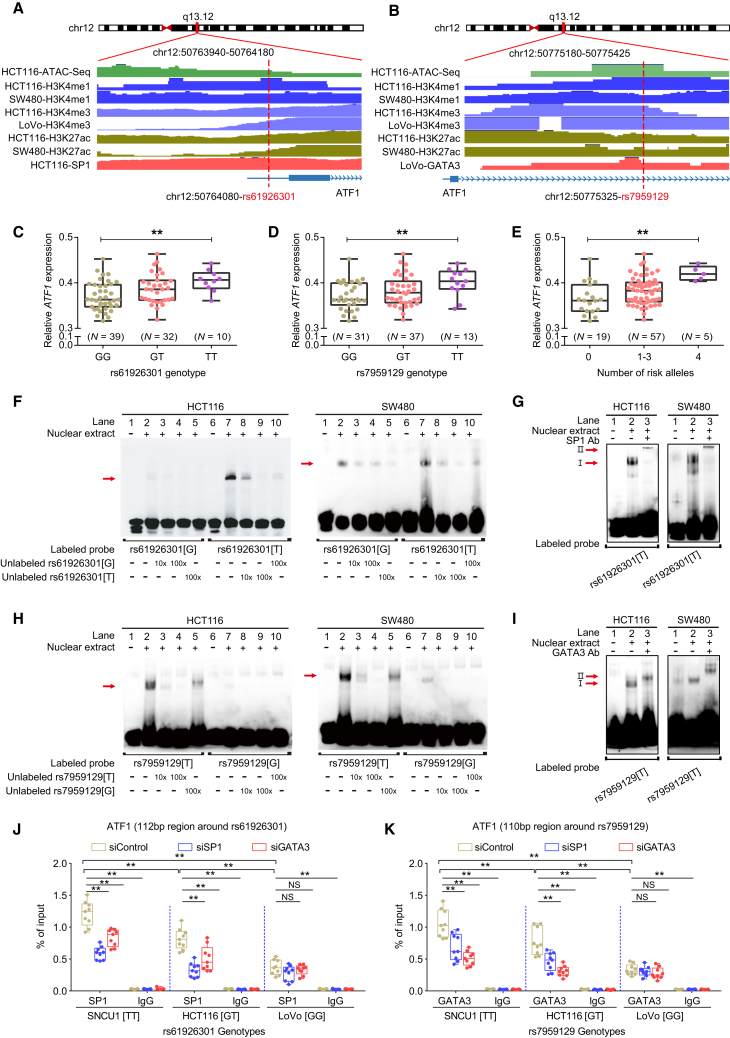
Figure 3.
SP1 and GATA3 preferentially bind to the dbSNP: rs61926301[T] and dbSNP: rs7959129[T] alleles at the ATF1 promoter and first intron region, respectively
(A and B) Epigenetic annotation for the region surrounding dbSNP: rs61926301 (D) or dbSNP: rs7959129 (E) in CRC cell lines. Data including ATAC-seq peaks, TF (SP1 or GATA3) peaks, and multiple histone (H3k4me1, H3K4me3, and H3k27ac) modification peaks were obtained from the ENCODE database.
(C–E) eQTL analyses of ATF1 expression with the dbSNP: rs61926301 genotype (A), the dbSNP: rs7959129 genotype (B), and number of both risk alleles from our CRC patient samples. Data were shown as the mean ± SD and all ∗∗p < 0.01 values were calculated by linear regression analysis.
(F–I) EMSAs and SP1 and GATA3 super-shift EMSAs with biotin-labeled probes containing dbSNP: rs61926301 (F and G) or dbSNP: rs7959129 (H and I) in HCT116 and SW480 cells. Arrows indicate allele-specific bands that interact with nuclear protein in the cells. “I” represents the allele-specific binding band. “II” represents the super-shifted band. In addition, 10× and 100× respectively represent 10-fold and 100-fold excess amounts of an unlabeled probe compared with the amount of the labeled probe. “+” and “−” indicate added and not added, respectively.
(J and K) The binding of SP1 and GATA3 to the region surrounding dbSNP: rs61926301 (J) or dbSNP: rs7959129 (K) was measured by ChIP-qPCR assays in the SNU-C1, HCT116, and LoVo cell lines, which carry different genotypes of both SNPs. Data were presented as the mean ± SD from three repeated experiments, each with three replicates. All ∗∗p < 0.01 values were derived from a comparison with controls via a two-sided Student’s t test.