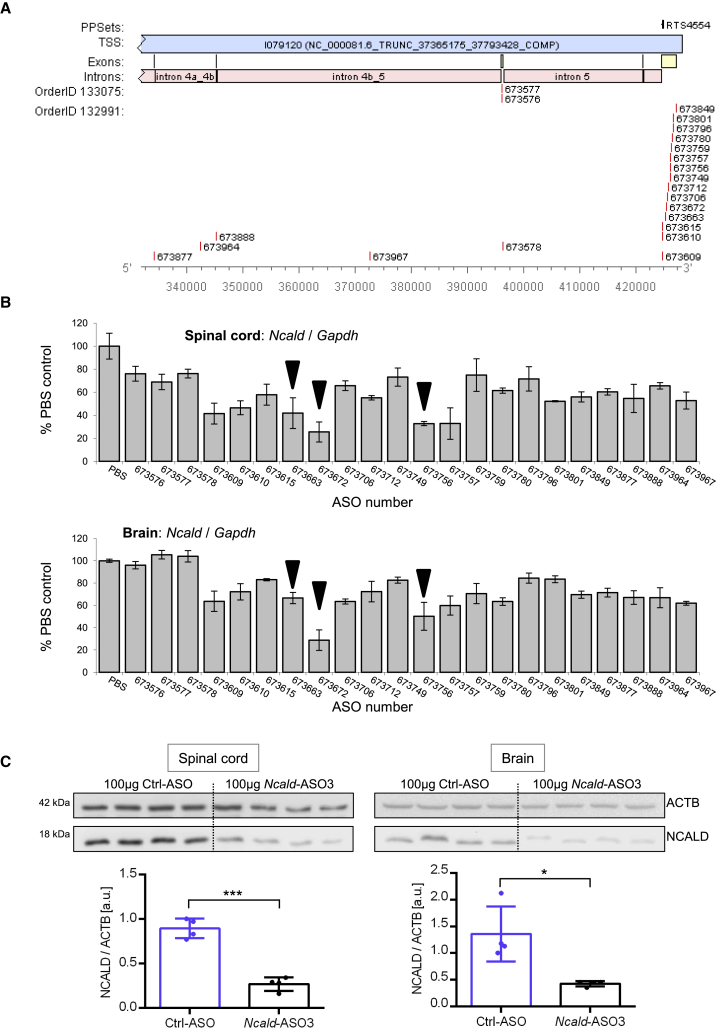
Figure 1.
Target Regions of Tested Ncald-ASOs and Knockdown Efficiency in Spinal Cord and Brain of Adult Wild-Type Mice
(A) Numbers of generated Ncald-ASOs and their respective target site in the mouse Ncald gene are shown. Used reference sequence is the Mus musculus strain C57BL/6J chromosome 15, GRCm38.p4 C57BL/6J (GenBank: NC_000081.6). Exons are labeled in yellow, introns in pink.
(B) The 22 most efficient Ncald-ASOs were applied in adult wild-type mice by intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) bolus injection and knockdown efficiency was determined by qRT-PCR of Ncald (primer probe set flanks exon 5–6 junction) relative to Gapdh (control) expression in spinal cord and brain. Ncald-ASOs marked by black triangle were tested in neonatal mice.
(C) NCALD protein levels in the spinal cord and the brain of P10 animals (n = 4 animals per genotype) treated i.c.v. at P2 with 100 μg Ncald-ASO3 were more than 70% reduced compared to mice injected with 100 μg of Ctrl-ASO. Numbers on the left indicate respective band size in kDa. ACTB, loading control. Unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.