Figure 1.
Identification of Expanded GGC Repeat within NOTCH2NLC in Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease
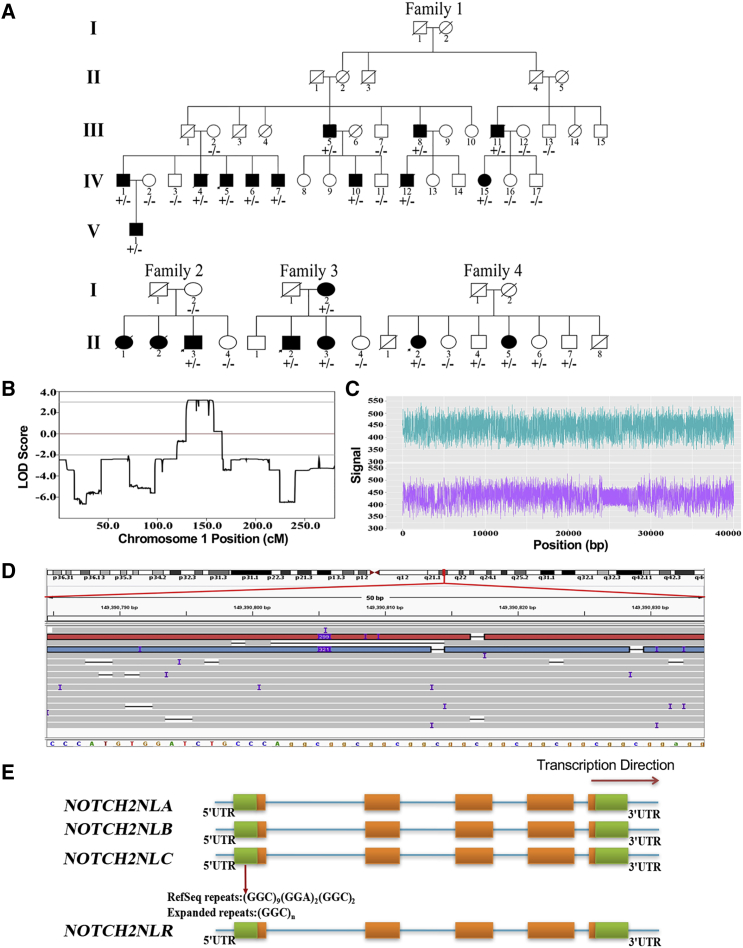
(A) Pedigrees of neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID)-affected families and corresponding individual genotypes.
(B) Genetic linkage analysis indicated maximum logarithm of odds (LOD) scores 3.184 in chromosome 1, a 49.8-Mb region at 1p13.3-q23.1 (chr1:109260034-159016186).
(C and D) GGC expansions detected by LRS. Nanopore electric signal (C) from subject F1-IV:15 indicated GGC expansions in the lower lane compared to the normal allele in the upper lane. More than ten reads covering the causative region were seen in the Integrative Genomics Viewer for subject F1-IV:15. Two reads were determined to carry the “insertion” variation (chr1:149390803-149390842, hg38 version), corresponding to the GGC triplet expansion in NOTCH2NLC (D).
(E) Schematic representation of the causal variant in NOTCH2NLC: a certain number of GGC triplets exist in 5′ UTR of NOTCH2NLC in healthy individuals, and large expanded GGC triplets are present in affected individuals.