Figure 1.
D Domain Selection
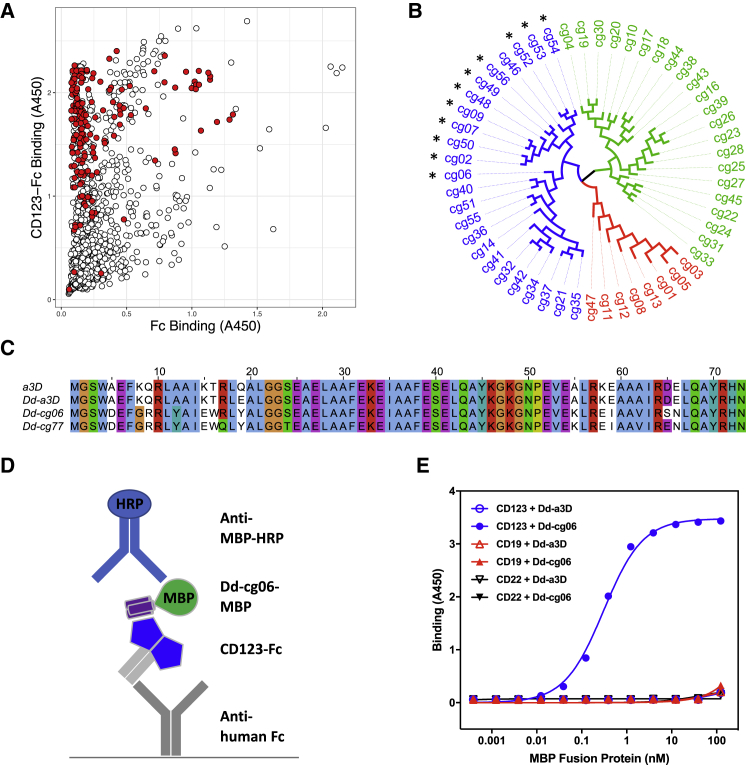
(A) ELISA binding data from naive phage library screen. Individual phage clones were assayed for binding to both human CD123-Fc (CD123-Fc)- and human Fc alone (Fc)-coated wells. Bound phage were detected with anti-M13-HRP. A total of 1,261 D domains were screened, yielding 1,052 unique sequences. Clones representing a diversity of sequence relatedness (shown in red) were selected for further characterization. (B) Dendrogram of D domain clone sequences converted to MBP fusions and/or CARs for further characterization. Colors indicate three distinct sequence families, referred to as F3 (blue), F1 (green), and C2 (red). CARs promoting NFAT activation in Jurkat reporter assay are indicated with an asterisk. (C) Sequence alignment of α3D (a3D), the parental D domain (Dd-a3D), the naive CD123-binding D domain (Dd-cg06), and the derived, deimmunized variant (Dd-cg77). Clustal X color scheme used for alignments in Jalview.49 (D) A schematic representation of MBP ELISA. (E) Results of MBP ELISA. Equimolar concentrations of Fc fusion of CD123, CD19, and CD22 were captured with anti-human Fc. Bound Dd-cg06-MBP (Dd-cg06) or Dd-a3D-MBP (Dd-a3D) proteins are detected with anti-MBP-HRP. Dd-cg06 binds to CD123-Fc, but not CD19-Fc or CD22-Fc. The parental D domain, Dd-a3D, is a poor binder of any target protein tested.