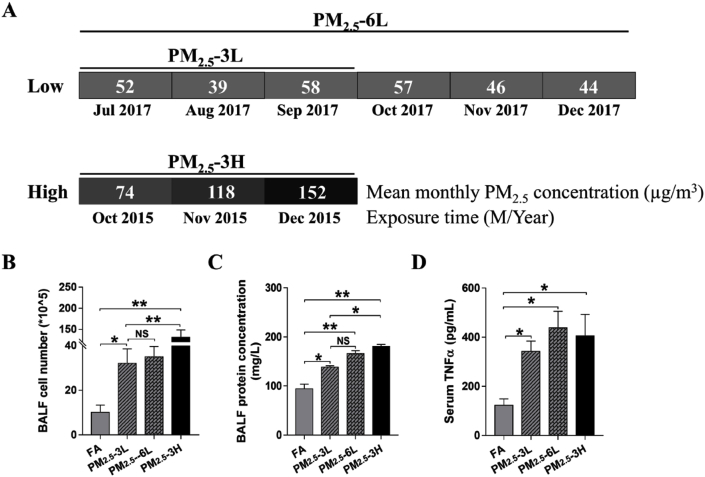
Fig. 1.
Effect of exposure time and concentration on PM2.5-induced systematic inflammation and lung injury. PM2.5 concentration of Wanliu monitoring station was recorded during the exposure period. Mean monthly PM2.5 concentration of July, August, September, October, November and December in 2017, as well as October, November and December in 2015 were shown (A). After exposure to filtered air (FA), low concentration of PM2.5 for 3–6 months (PM2.5–3L, PM2.5–6L) or high concentration of PM2.5 (PM2.5–3H) for 3 months, total cell number (B) and protein content (C) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and serum TNFα level was measured (D). Data are presented as the means ± SEM. N = 3–4. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; NS, not significant.