Figure 4.
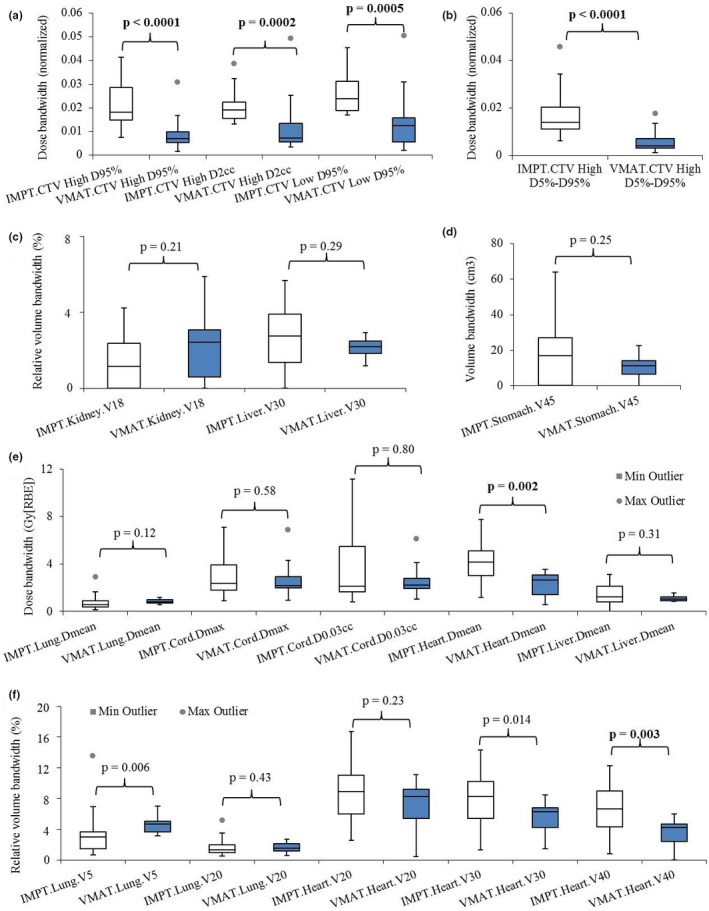
Comparison of plan robustness between intensity‐modulated proton therapy (IMPT) and volumetric‐modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plans using the widths of the dose volume histogram (DVH) band pairs in the presence of uncertainties. (a) clinical target volume (CTVhigh) D95% and , and CTVlow D95% normalized to the prescription dose. (b) CTVhigh D5%‐D95% normalized to the prescription dose. (c) Kidney V18Gy[RBE] and liver V30Gy[RBE] in relative volume. (d) Stomach V45Gy[RBE] in absolute volume. (e) Lung Dmean, cord Dmax and , heart Dmean, and liver Dmean in absolute dose. (f) Lung V5Gy[RBE] and V20Gy[RBE], heart V20Gy[RBE], V30Gy[RBE] and V40Gy[RBE] in relative volume. In each box plot, the five horizontal lines from top to bottom are the maximum, third quartile, median, first quartile, and minimum value of the DVH band widths in the presence of uncertainties of the corresponding DVH index for the whole group excluding the outliers respectively. The grey points are the outliers as defined in Statistical Analysis subsection. Numbers at the top of the columns are P‐values from Wilcoxon rank sum testing. The blue boxes are the IMPT results and white boxes are the VMAT results. Abbreviations: RBE = relative biological effectiveness.
