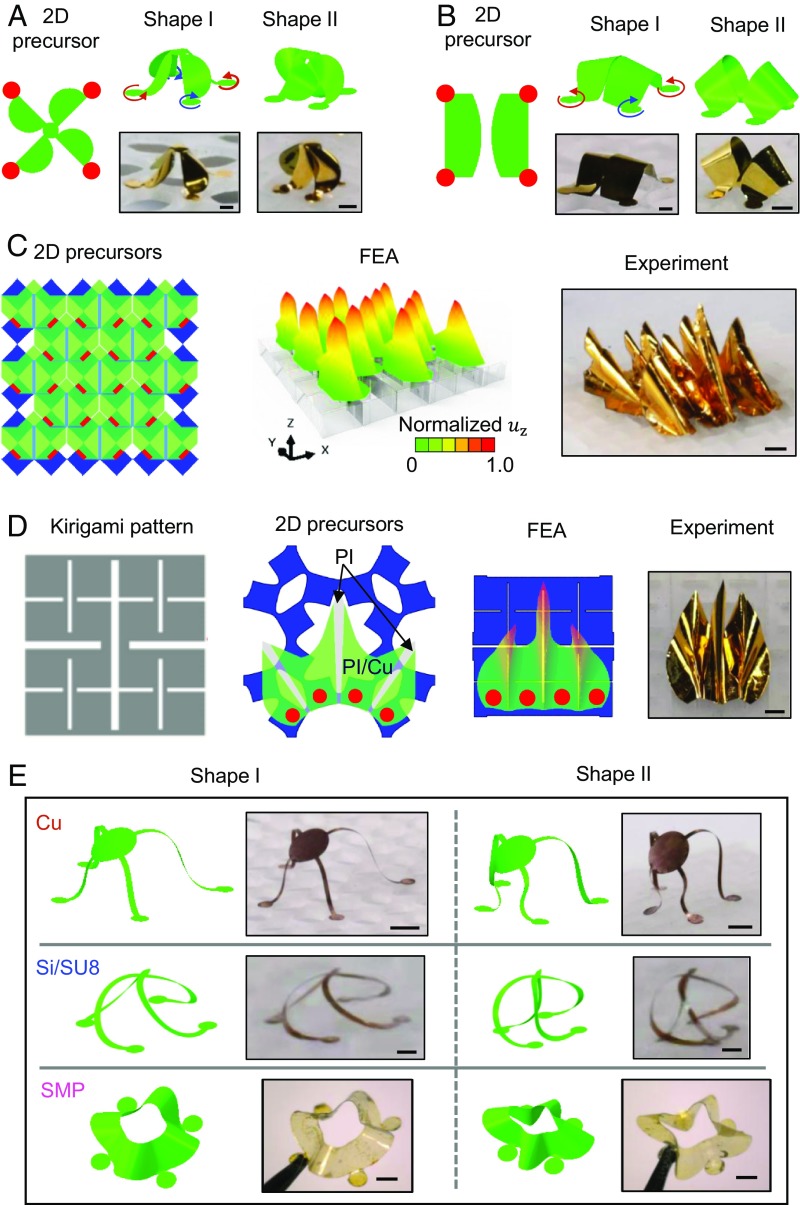
Fig. 3.
Three-dimensional morphable mesostructures based on buckling and twisting with diverse geometries and materials. (A) Two-dimensional geometries, FEA predictions, and experimental images (optical) of a morphable 3D chiral, propeller structure. (B) Two-dimensional geometries, FEA predictions, and experimental images (optical) of a morphable 3D box structure. Shape I and shape II correspond to the 3D shapes after releasing of the stretching mode (prestrain from 100 to 40%) and releasing of the rotating mode (prestrain from 40 to 0%). (C) Two-dimensional geometries, FEA predictions (showing normalized displacements in z direction), and experimental images (optical) of an array of creased structures based on twisting-induced folding. (D) Two-level square substrate cut pattern, 2D geometries, FEA predictions, and experimental images (optical) of a structure with multiple creases. (E) FEA predictions and experimental images (optical) of 3 mesostructures constructed with diverse materials. Scale bars, 1 mm for structures in A–D; 2 mm for Cu structures (E, Top); and 500 μm for Si/SU8 and SMP structures (E, Middle and Bottom).