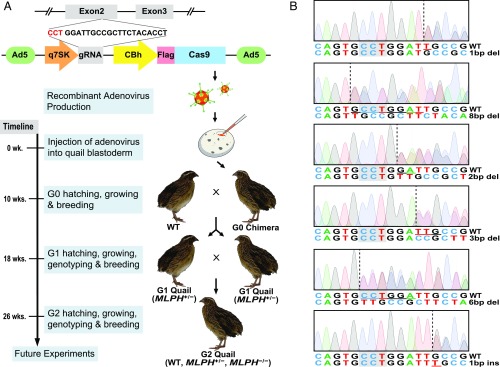
Fig. 1.
Generation of targeted gene knockout quail using adenovirus. (A) Schematic representation of research plan. gRNA of the MLPH gene was selected from exon 2, and the adenoviral CRISPR/Cas9 vector was constructed. Recombinant adenovirus was subsequently produced and injected into the quail blastoderm. Chimeras (G0) were maintained and mated with wild-type (WT) quail to produce G1 quail with a heterozygous genotype of the MLPH gene (MLPH+/−). Male and female G1 MLPH+/− quail were subsequently mated to generate G2 quail with a homozygous genotype of the MLPH gene (MLPH−/−). After production of the recombinant adenovirus, it took a total of 10 wk, 2 wk for egg incubation after virus injection and another 8 wk for sexual maturation, to receive eggs from G0 quail. After G1 quail hatched, the MLPH+/− quail were screened and mated to produce G2 offspring 8 wk later. Fully grown G2 offspring were obtained for further experiments 26 wk after the injection of the adenovirus. (B) Sanger sequencing chromatograms of G1 MLPH+/− quail. Dashed lines indicate the starting point of the mutation, and the deleted or inserted nucleotides are underlined. The PAM sequences are highlighted in gray. Nucleotide sequences are presented in a negative direction.