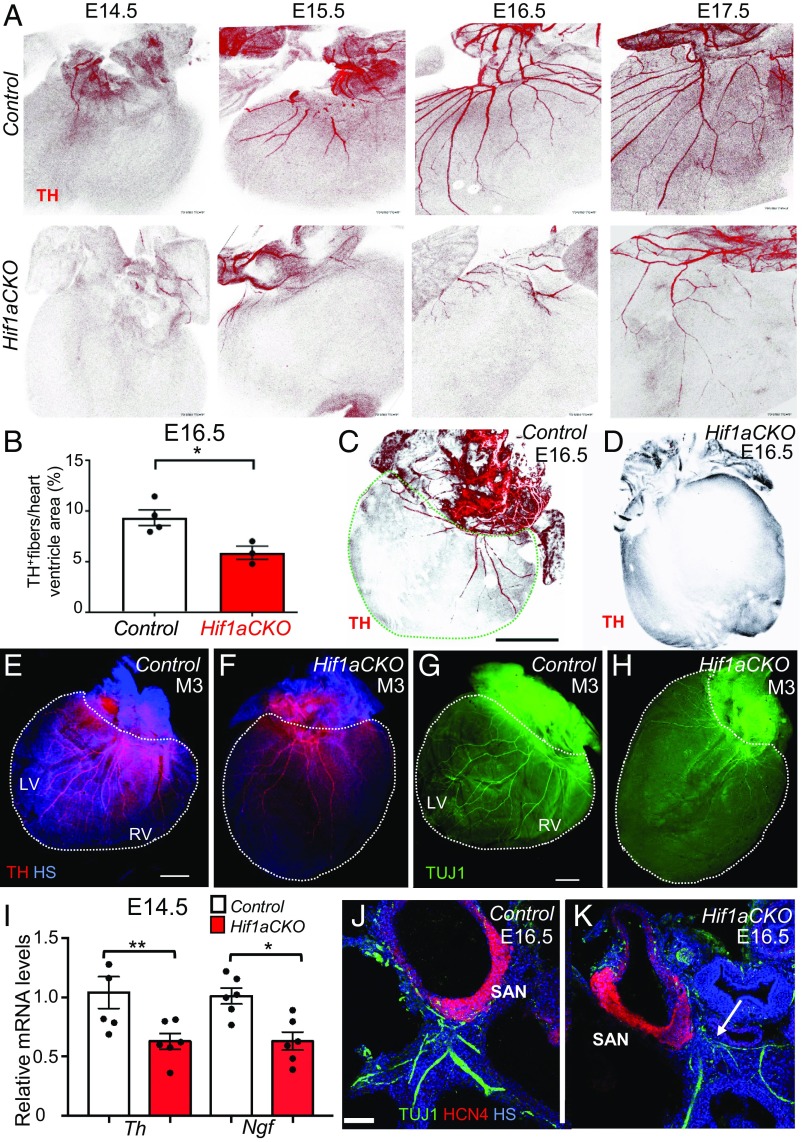
Fig. 3.
Impaired sympathetic innervation of Hif1aCKO hearts. (A) Immunohistochemical staining of TH in posterior view of hearts from control (Upper) and Hif1aCKO (Lower) littermate embryos between E14.5 and E17.5. (B) Quantification of TH+ fibers per ventricle area in E16.5 control and Hif1aCKO hearts (n = 4 each). *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. (C and D) Posterior view of E16.5 control heart (C) and Hif1aCKO heart with no detectable TH+ fibers (D). In C, the dashed green line demarcates the ventricular area of the heart. (Scale bar: 500 μm.) (E–H) Sympathetic innervation of hearts from 3-mo-old male mice (M3) was analyzed by anti-TH (E and F) and anti-TUJ1 (G and H) immunohistochemistry. The posterior view is shown, and dotted lines encompass the left ventricle (LV) and right ventricle (RV) of the heart. (Scale bar: 1 mm.) (I) Relative Th and Ngf mRNA levels were measured by reverse-transcription and qPCR, using mRNA extracted from the whole heart at E14.5, when the sympathetic neurons reach the heart and start to innervate the ventricles (n = 8 hearts per genotype). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student’s t test. (J and K) Expression of HCN4, a marker for the cardiac conduction system, in E16.5 heart sections. HCN4+ area of the SAN in the Hif1aCKO embryo is comparable to that in the control embryo at E16.5, but TUJ1-labeled nerve fibers in proximity of the SAN are reduced, thinner, and more disorganized in the Hif1aCKO (arrow) compared with control heart. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) HS, Hoechst stain. All numerical data are presented as mean ± SEM.