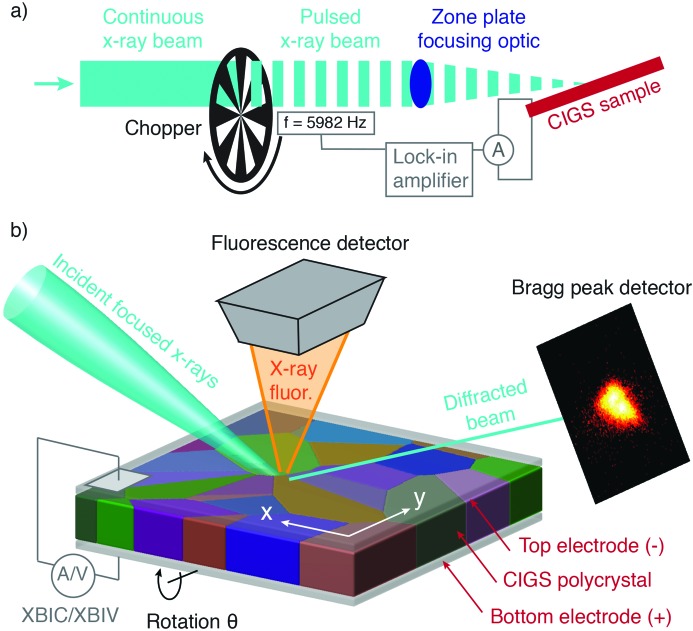
Figure 1.
A schematic of the experimental setup. Panel (a) shows the integration of an optical chopper and lock-in amplifier into the X-ray beamline that enables position-resolved XBIC and XBIV measurements. Panel (b) shows more details of the sample–beam interaction area: a PV device containing an active layer of polycrystalline CIGS between top and bottom electrodes was illuminated with a nanofocused X-ray beam. The orientation of the beam was such that a 112 Bragg peak could be observed from grains that were favorably oriented. Raster scans of the sample were performed by displacing the sample in the plane of the film in ∼100 nm steps. During the raster scan simultaneous measurements were performed of the local Bragg diffraction, the emitted X-ray fluorescence spectrum, and either the XBIC or XBIV. To measure 3D Bragg peak information, raster scans were repeated at different incident angles by varying the sample angle (along the θ rotation axis in the figure).