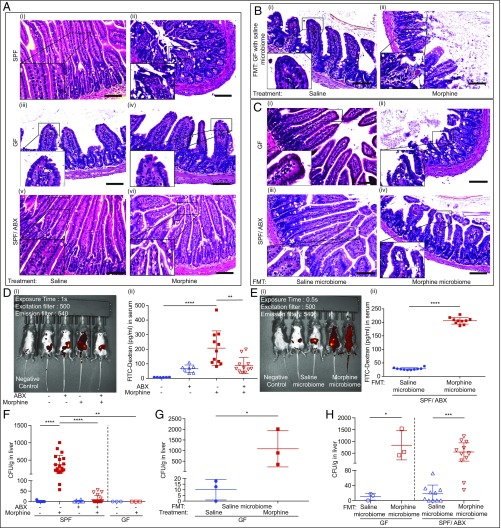
Fig. 2.
Gut microbiome is responsible for gut permeability and bacterial translocation induced by morphine. (A–C) Representative H&E stained section of mouse ileum. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) WT and ABX mice: nSPF = 10, nGF = 3. (D and E) Representative images and summary of FITC-dextran fluorescent signal distribution in mice; n = 6 to 11. (F) Bacterial colony-forming unit (CFU) in liver homogenates of GF and SPF mice; nSPF = 10 to 20; nGF = 3. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. (G) CFU from GF mice reconstituted with normal gut microbiota and treated with either morphine or saline; nGF = 3. (H) CFU from GF mice and ABX-treated SPF mice received gut microbiota either from saline or morphine-tolerant donors; nGF = 3; nSPF/ABX = 10 to 12. Data were analyzed by Student’s t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Mean ± SD.