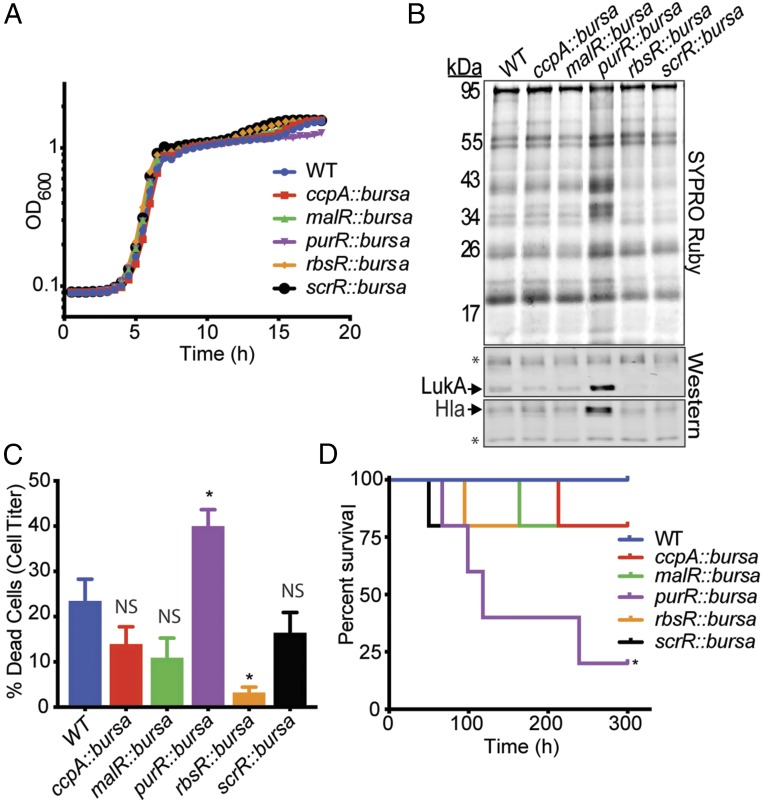
Fig. 1.
Phenotypic screen for virulence reveals that purR transposon mutants are hypervirulent. (A) LacI family regulator mutants were assessed for their ability to grow in TSB. Each strain showed similar growth kinetics as determined by OD600 (three replicates per strain). (B) Supernatants from exponentially grown purR::bursa exhibit a greater number of secreted proteins compared with the profiles of the other LacI family regulator mutants. purR::bursa also produced higher levels of the toxins Hla and LukAB. Asterisks indicate loading controls, which are nonspecific bands recognized by the antibodies. (C) Five percent culture filtrates obtained from purR::bursa were more cytotoxic toward primary human PMNs than those of wild-type USA300 or LacI family regulator mutants (n = 5 human donors). Statistical significance was done using a one-way ANOVA and post hoc Holm–Sidak correction of multiple comparisons. Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05. NS, not significant. (D) Mice infected i.v. (2.5 × 107 CFUs) with each LacI mutant or wild-type USA300 succumb to infection with the purR::bursa mutant at a faster rate than that of any other strains tested. Statistical analysis of survival differences between wild type and purR::bursa was performed using the Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test. *P < 0.05.