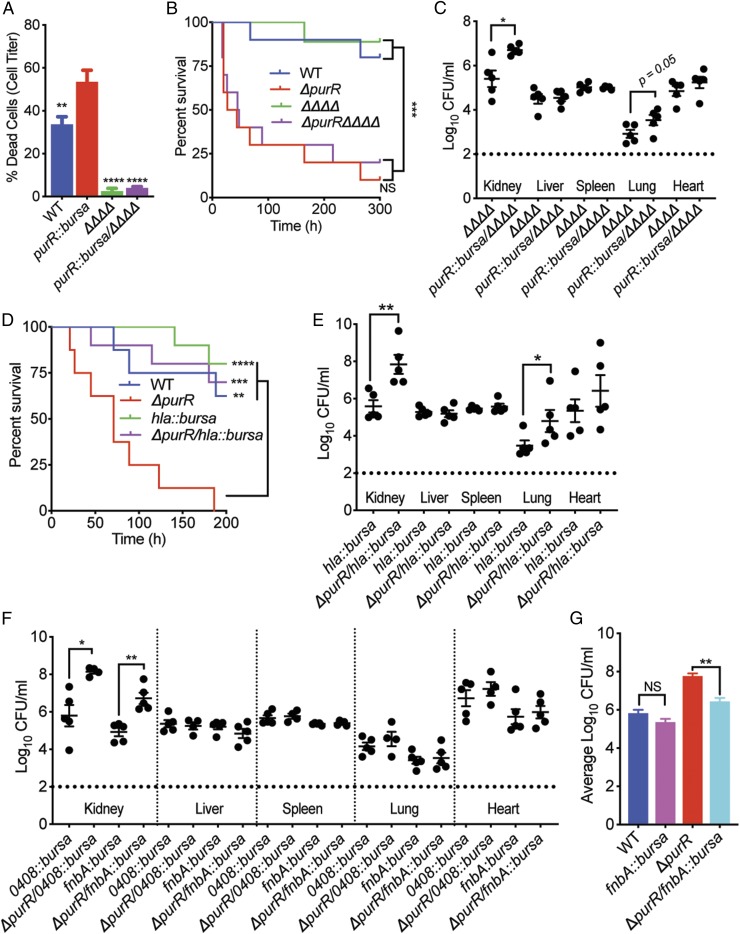
Fig. 6.
purR mutant relies on a set of secreted factors to drive its heightened pathogenesis. (A) PMNs intoxicated with 1.25% supernatants no longer display an elevated susceptibility to supernatants derived from the purR mutant in the absence of the bicomponent pore-forming leukocidins (ΔpurR/ΔΔΔΔ) (n = 3–6 donors). Statistical significance was done using a one-way ANOVA and post hoc Holm–Sidak correction of multiple comparisons. Error bars indicate SEM. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. (B) Mice infected i.v. (2.5 × 107 CFUs) with the ΔpurR/ΔΔΔΔ mutant do not demonstrate a reduction in susceptibility to death despite the loss of the leukocidins (n = 10 mice per strain). Statistical analysis for survival was performed using the Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test with P values adjusted for multiple comparisons. ***P < 0.001. NS, not significant. (C) Mice infected i.v. (1 × 107 CFUs) with the ΔpurR/ΔΔΔΔ mutant do not demonstrate a reduction in bacterial burden at 20 h postinfection compared with the parental ΔΔΔΔ strain (n = 5 mice per strain). Statistical analysis was examined using a two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test between each infected organ. *P < 0.05. (D) Alpha-toxin drives the purR mutant lethality phenotype in mice. Mice infected i.v. (2.5 × 107 CFUs) with the ΔpurR/hla::bursa mutant are no longer susceptible to death in a purR mutant-dependent manner. Statistical analysis for survival was performed using the Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test with P values adjusted for multiple comparisons. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. (E) Mice infected i.v. (2.5 × 107 CFUs) with the ΔpurR/hla::bursa mutant do not demonstrate a reduction in bacterial burden at 20 h postinfection compared with the parental hla::bursa strain (n = 5 mice per strain). Statistical analysis was examined using a two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test between each infected organ. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (F) FnbA contributes to the increased bacterial burden phenotype of the purR mutant at 20 h postinfection. Mice infected i.v. (2.5 × 107 CFUs) with mutants for SAUSA300_0408 and fnbA in the purR mutant background were assessed for bacterial burden and only the ΔpurR/fnbA::bursa mutant demonstrated a drop in CFUs within the kidneys (n = 5 mice per strain). Statistical analysis was examined using a two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test between each infected organ. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (G) FnbA significantly contributes to the enhanced bacterial burden phenotype exhibited by the purR mutant. CFU outputs from the kidneys of i.v. infected mice were aggregated and compared (n ≥ 10 mice per strain). Statistical significance was calculated using two-tailed t tests comparing either wild-type USA300 with fnbA::bursa or ΔpurR with ΔpurR/fnbA::bursa. **P < 0.01. NS, not significant.