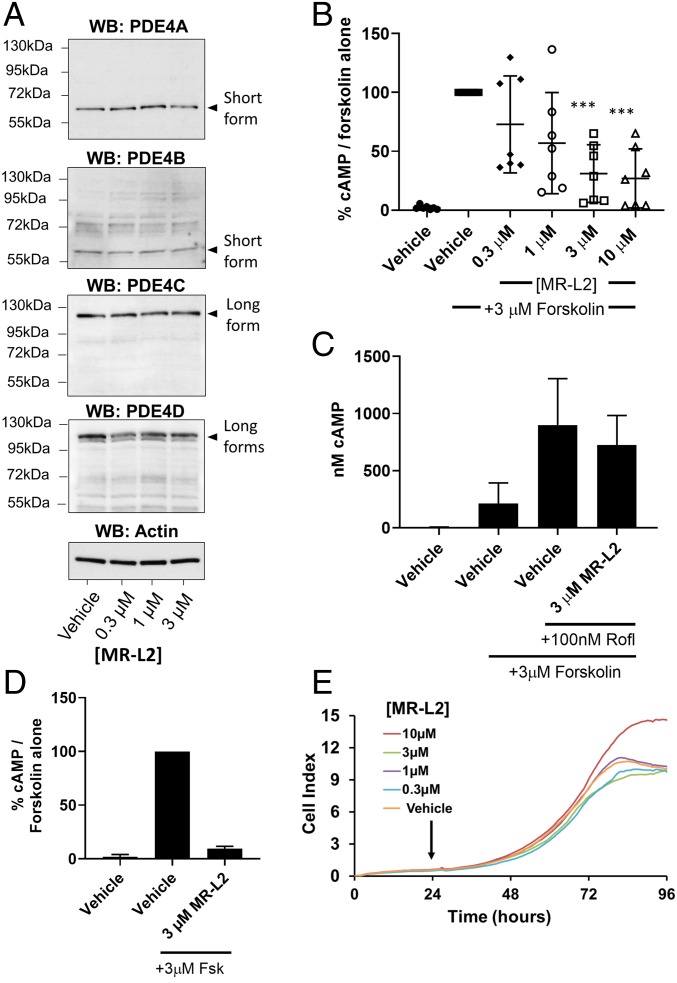
Fig. 3.
MR-L2 reduces intracellular cAMP in MDCK cells without affecting PDE4 expression or cell viability. (A) MDCK cells were grown in 2D culture and treated with increasing concentrations of MR-L2. Western blot analysis of protein extracts shows the expression of short-form PDE4A and PDE4B and PDE4D, as well as long forms of PDE4C and PDE4D. Based upon their observed gel migration and predicted molecular weights, these bands are likely to represent PDE4A1, PDE4B2, PDE4C1/3, PDE4D1/2, PDE4D5/7, and PDE4D3/8/9 (in some cases, multiple isoform variants comigrate due to similar molecular weights). The expression of these isoform variants was not affected by 1-h incubation with MR-L2. β-Actin was used as a protein loading control. Quantitation of multiple Western blot analysis is presented in SI Appendix, Fig. S2E. (B) A 1-h pretreatment with MR-L2 suppresses cAMP accumulation in response to acute treatment with 3 µM forskolin (15 min). Mean of n = 7 independent experiments (±SD). Data points represent independent experimental results. (C) The suppressive effects of 1-h pretreatment with 3 µM MR-L2 on forskolin (3 µM, 15 min)-stimulated cAMP accumulation was ablated by cotreatment with the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast (100 nM). Results show the mean of three independent experiments, and error bars represent SD. (D) Extracellular cAMP was assessed in response to MR-L2 (3 µM) incubation for 1 h before forskolin (3 µM, 15 min) challenge. Extracellular cAMP accumulation was reduced in the MR-L2 samples, indicating that the intracellular reduction in global cAMP was not due to enhanced excretion from the cell. Data from three independent experiments are shown. (E) MR-L2 treatment exhibited no deleterious effects on the proliferation of MDCK cells in 2D culture using the xCELLigence impedance-based assay system. MR-L2 was added to the culture 24 h after inception of the assay.