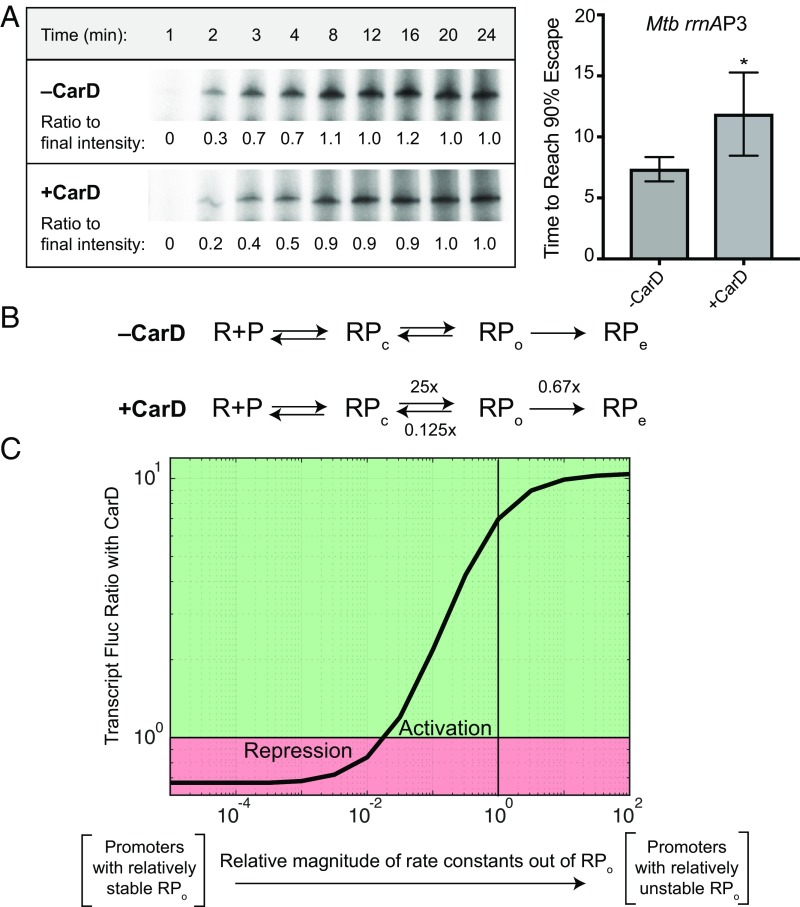
Fig. 2.
CarD slows promoter escape from the Mtb rrnAP3 promoter. (A) Single-round in vitro promoter escape assay results with representative gel images showing the time-dependent increase in 32P-labeled RNA transcripts formed by M. bovis RNAP from the Mtb rrnAP3 promoter construct in the presence and absence of CarD. Promoter escape rate is quantified by the time until 90% of the final transcript intensity is reached (t90%). The graph shows the mean t90% ± SEM (−CarD n = 3; +CarD n = 7). Statistical significance was analyzed by Welch’s t test. *P < 0.05. (B) A proposed kinetic model in which CarD accelerates the rate of transcription bubble formation (RPc→RPo) 25-fold, slows the rate of bubble collapse (RPo→RPc) 8-fold, and slows the rate of promoter escape (RPo→RPe) 1.5-fold. Effects of CarD on rates were chosen based on experimentally determined values. (C) Graph showing the mRNA flux ratio from a given Mtb promoter on the addition of CarD. The X-axis represents a titration of the rate constants out of RPo relative to the kinetic model for rrnAP3. Calculations were performed with the kinetic model of CarD activity on a set of hypothetical promoters with a titration of RPo stability, using the web-based tool described in ref. 25. The green region represents promoters that would be activated by CarD; the red region represents promoters that would be repressed.