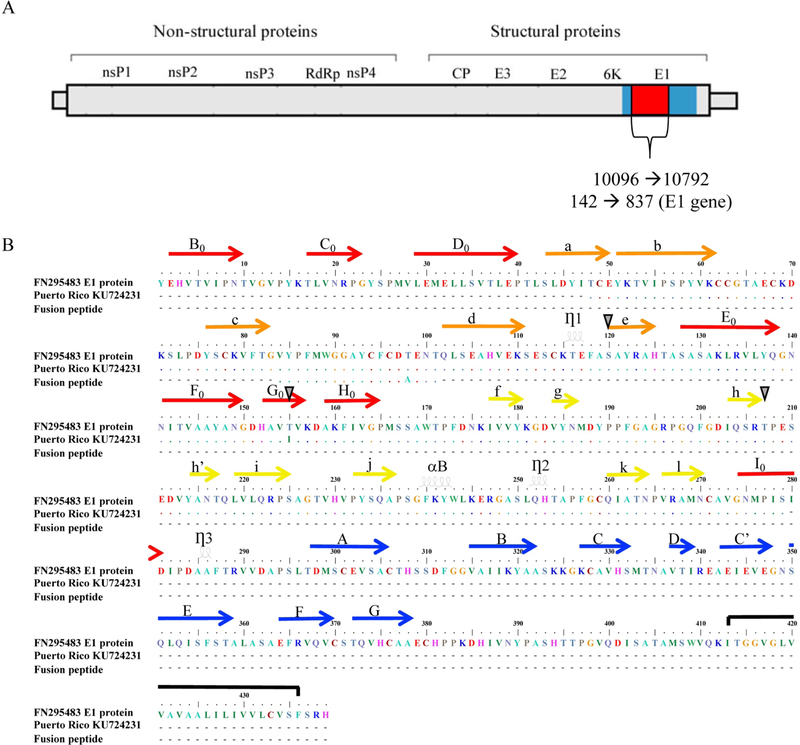
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of the CHIKV genome and the E1 glycoprotein. Panel A: The position of the CHIKV full-length E1 gene and the 696 nucleotides analyzed in this study are denoted in reference to the complete genome. Panel B: The top line represents the CHIKV isolate MY/06/37348 (Malaysia, 2006) reference sequence FN295483. The second line is the PR sequence KU724231, which includes the mutation T155I as an example. The third line represents the E1 fusion peptide. The domains are identified according to Roussel et al. (52). The arrows represent the b sheets within each domain. Red arrows indicate E1 domain I; yellow arrows indicate domain II; and blue arrows indicate domain III. Orange arrows indicate domain II regions that are located within domain I. The loops indicate the a helices. The black line shows the transmembrane region. Sites of unique mutations detected in the sequences from PR are denoted with a grey triangle.