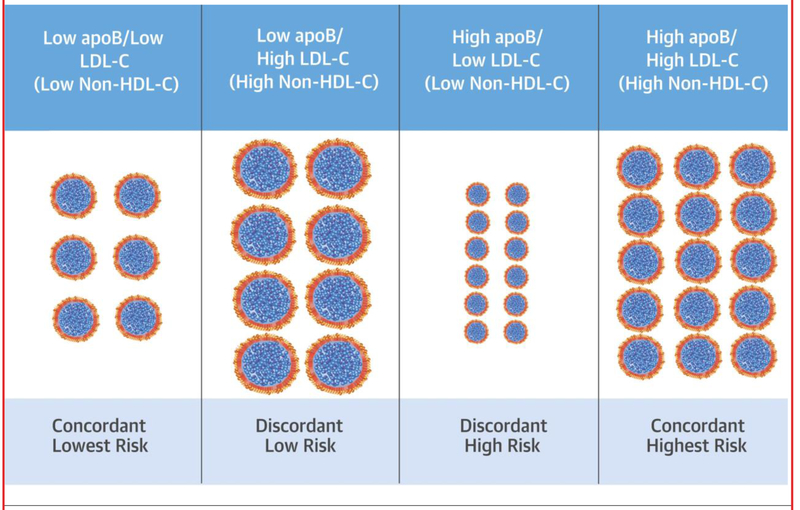
CENTRAL ILLUSTRATION. Apo B, LDL-C Discordance in Young Adults Is Associated With Coronary Artery Calcification in Mid-Life: The Biologic Basis for Discordance Analysis.
When apolipoprotein B (apoB) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (or non–high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [non–HDL-C]) are concordant within an individual (columns 1 and 4), apoB particles contain an average amount of cholesterol. When concordant, apoB, LDL-C, and non–HDL-C predict risk similarly well. When apoB and LDL-C (or non–HDL-C) are discordant, the particles are either cholesterol-enriched (column 2), or cholesterol-deplete (column 3). In discordant groups, the risk for subclinical atherosclerosis appears more strongly associated with apoB than with LDL-C or non– HDL-C.