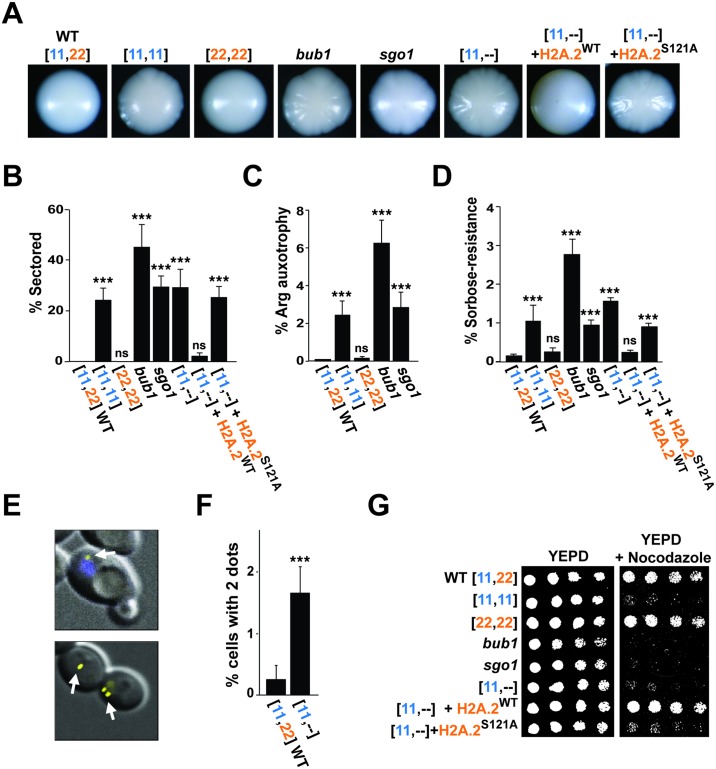
Fig 2. A C. albicans mutant lacking H2A.2 phenocopies spindle-checkpoint mutants.
(A and B) Deletion of H2A.2, BUB1, or SGO1, or replacement of H2A.2 with an H2A.2 S121A mutation, results in similar colony sectoring phenotypes. Colony morphology (A) and percent of colony sectoring (B) are shown for WT C. albicans, the [11,11] strain that lacks H2A.2, the [22,22] strain that lacks H2A.1, knockouts of the spindle-checkpoint genes, BUB1 and SGO1, and [11,--], [11,--]+H2A.2WT, and [11,--]+H2A.2S121A strains. (C, D, E, and F) Mutants lacking H2A.2, BUB1, or SGO1 display increased aneuploidy. (C) Percent of colonies that have lost the ability to grow on arginine-deficient medium, relative to growth on YEPD. Strains were plated on arginine-deficient medium or YEPD after 4 days on presporulation medium. Because these ARG4/Δ strains contain the ARG4 gene on only 1 copy of Chromosome 7, loss of that copy renders cells auxotrophic for arginine. (D) Percent of colonies that grow on sorbose-containing medium, relative to growth on YEPD. Because cells with both copies of Chromosome 5 are killed by sorbose, this medium selects for cells that have lost 1 copy of the chromosome. (E, top panel) Superimposed fluorescence and phase microscopy of QMY85, which contains approximately 120 tandem copies of the tet operator on one of its 2 Chromosome 5 homologs, as well as the Tet repressor fused to YFP. A yellow spot marks the tagged copy of Chromosome 5 (white arrow), and the nucleus is stained with DAPI (blue arrow). (Bottom panel) Example of neighboring cells that contain 1 spot (normal) or 2 spots (indicating an extra copy of Chromosome 5). (F) Percent of cells with 2 spots, counting only unbudded cells. (G) Sensitivity to the microtubule poison nocodazole (50 μM) shown by serial dilution. Please see S1 Data for the numerical values summarized in (B, C, D, and F). prespo, presporulation; WT, wild type; YEPD, yeast extract peptone dextrose; YFP, Yellow Fluorescent Protein.