FIGURE 3.
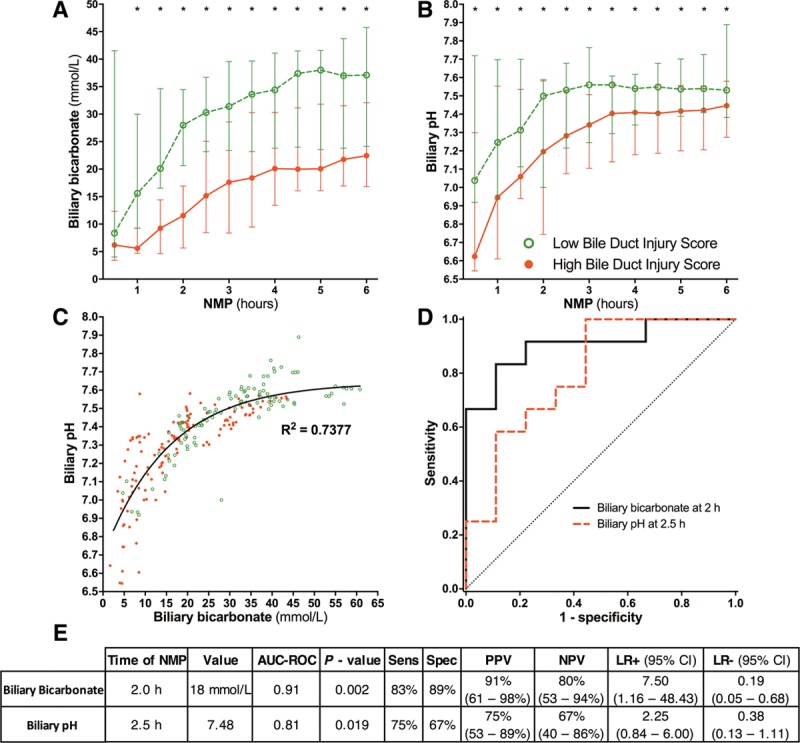
Biliary bicarbonate and pH produced during NMP correlated significantly with BDI. Biliary bicarbonate concentration (A) and biliary pH (B) were significantly higher in livers with a low BDI score, compared with livers with a high BDI score at each timepoint during NMP. C, Biliary pH and bicarbonate concentration were strongly correlated with each other. The line of best fit shows that in the lower range of biliary bicarbonate, small increases in biliary bicarbonate led to relatively large increases in biliary pH. At biliary bicarbonate greater than 30 mmol/L, biliary pH remained relatively stable despite further increases in bicarbonate concentration. (D) ROC curves and (E) statistical analyses of biliary bicarbonate and pH used to discriminate high and low BDI at the earliest timepoints. * P < 0.05. More detailed results, including calculations for all timepoints of bile collection during 6 hours of normothermic machine perfusion (NMP), are provided in Table S1, SDC (http://links.lww.com/TP/B649). AUC-ROC, area under the ROC curve; BDI, bile duct injury; CI, confidence interval; LR, likelihood ratio; NPV, negative predictive value; PPV, positive predictive value; ROC, receiver operating characteristics.
