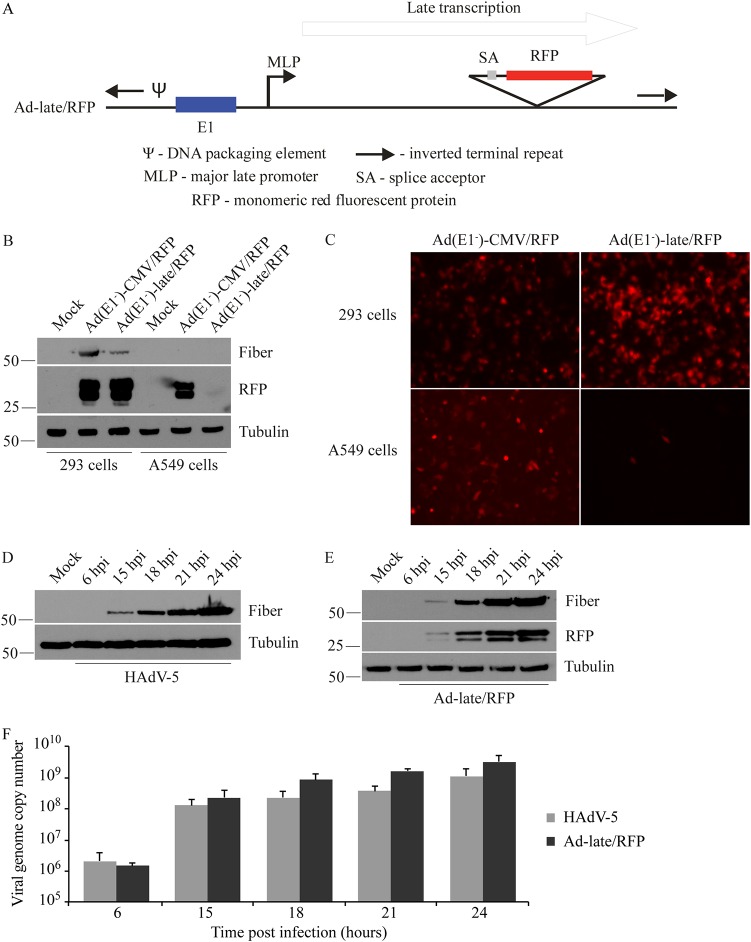
FIG 1.
Validation of the Ad-late/RFP construct. (A) Schematic diagram of Ad-late/RFP (not drawn to scale). The RFP cDNA is under the control of the HAdV MLP and the E1 region is present. An E1-deleted, replication-defective version of the Ad-late/RFP [referred to as Ad(E1–)-late/RFP] was also generated, which is able to replicate only in E1-complementing cells. (B) 293 and A549 cells were infected with Ad(E1–)-late/RFP or Ad(E1–)-CMV/RFP at an MOI of 1. The latter is a control virus with the ubiquitously expressed cytomegalovirus enhancer/promoter driving RFP expression. Whole-cell lysates were collected at 24 hpi for the detection of RFP, fiber (a positive control for HAdV replication), and tubulin (loading control). RFP from the Ad(E1–)-CMV/RFP is present in both 293 and A549 cell lysates independent of virus replication. However, RFP from Ad(E1–)-late/RFP is only present in 293 cells. (C) Cells were infected as in panel B, and fluorescence microscopy results at 24 hpi corroborate the selective expression of RFP from Ad(E1–)-late/RFP. (D to F) A549 cells were infected with HAdV-5 or Ad-late/RFP at an MOI of 10 for 6 to 24 h. (D and E) Fiber and RFP were detected by immunoblotting cell lysates. (F) qPCR was performed on genomic DNA isolated from infected cells, using oligonucleotide primers specific for the gene encoding capsid protein hexon (error bars represent the range of three independent experiments). As indicated by viral protein and DNA levels, Ad-late/RFP is able to grow as well as wild-type HAdV.