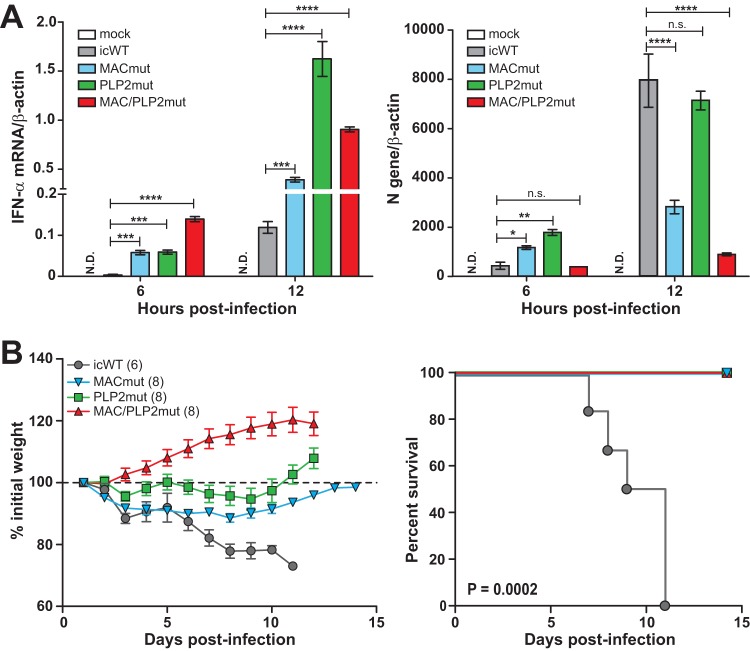
FIG 7.
Macrodomain mutant viruses induce type I interferon in primary macrophages and are attenuated in mice. (A) Mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages were infected with the indicated virus (MOI of 1) at 32°C. Total RNA was extracted at the indicated time points and subjected to RT-qPCR. The mRNA levels of IFN-α (left) and the N gene (right) are presented relative to that of β-actin. The results are representative of three independent experiments and were subjected to a two-tailed, unpaired t test. Error bars indicate ± SD. ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant; N.D., not detected. (B) Six-week-old mice were injected intracranially with either icWT or the indicated ts mutant virus (600 PFU/mouse) and monitored for weight loss. Viral pathogenicity was evaluated by body weight loss (left) and percent survival (right). The number (n) of infected mice is indicated in parentheses. Error bars indicate ± standard error of the mean. Differences in survival rates were calculated using a log-rank test.