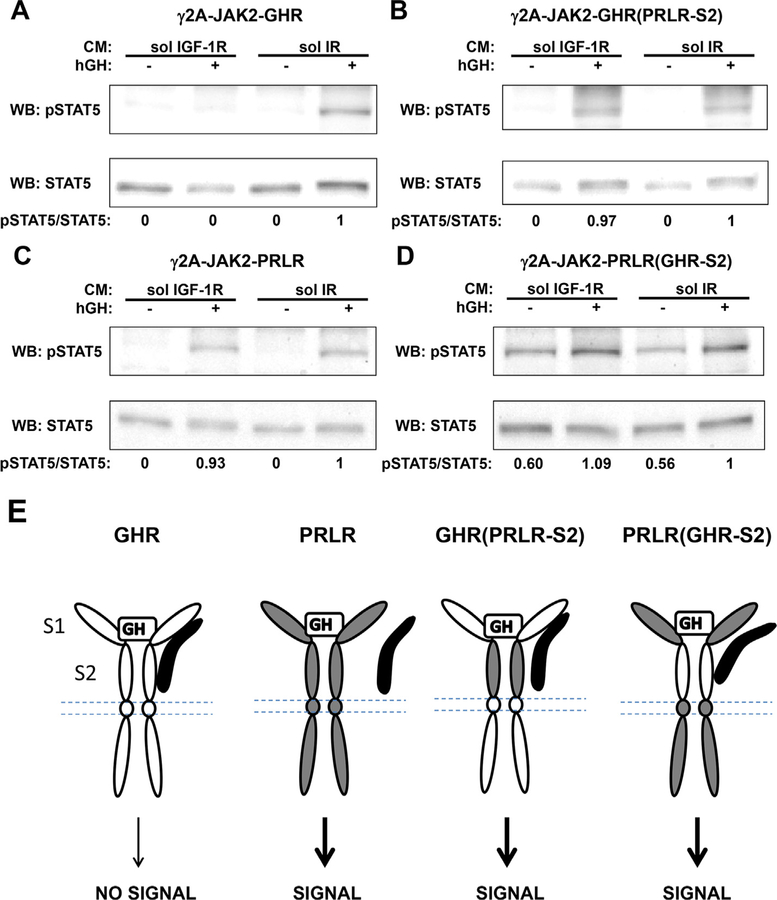
Fig. 5. Both S1 and S2 of GHR ECD are required for sol IGF-1R to inhibit GH-induced STAT5 activation.
A-D, Serum starved cells expressing GHR, PRLR, GHR(PRLR-S2), or PRLR(GHR-S2) were incubated with CM containing either sol IGF-1R (lanes 1 and 2) or sol IR (lanes 3 and 4), followed by treatment with vehicle (−) or hGH (+) at 500 ng/ ml for 10 min. Detergent extracts were immunoblotted for pSTAT5 and total STAT5 sequentially. The data shown are representative of three such experiments. Densitometric estimates of the relative intensity of the pSTAT5 band normalized by the abundance of total STAT5 (in arbitrary units with 1 as maximum control condition within the representative experiment) are shown.E, Diagrammatic summary and interpretation of findings. GHR is in white. PRLR is in gray. Soluble IGF-1R is in black. GH-induced signaling mediated by GHR, not PRLR, is subject to inhibition by sol IGF-1R. The GHR/sol IGF-1R association is cartooned as involving both the S1 and S2 of the GHR ECD. Such association could be direct or mediated by other unidentified molecule(s). Note that the association between sol IGF-1R and GHR(PRLR-S2) or PRLR (GHR-S2) is depicted as partial in this diagram, which is not sufficient to block downstream signaling. It remains possible that there is no interaction between sol IGF-1R and these chimera receptors.