Figure 5.
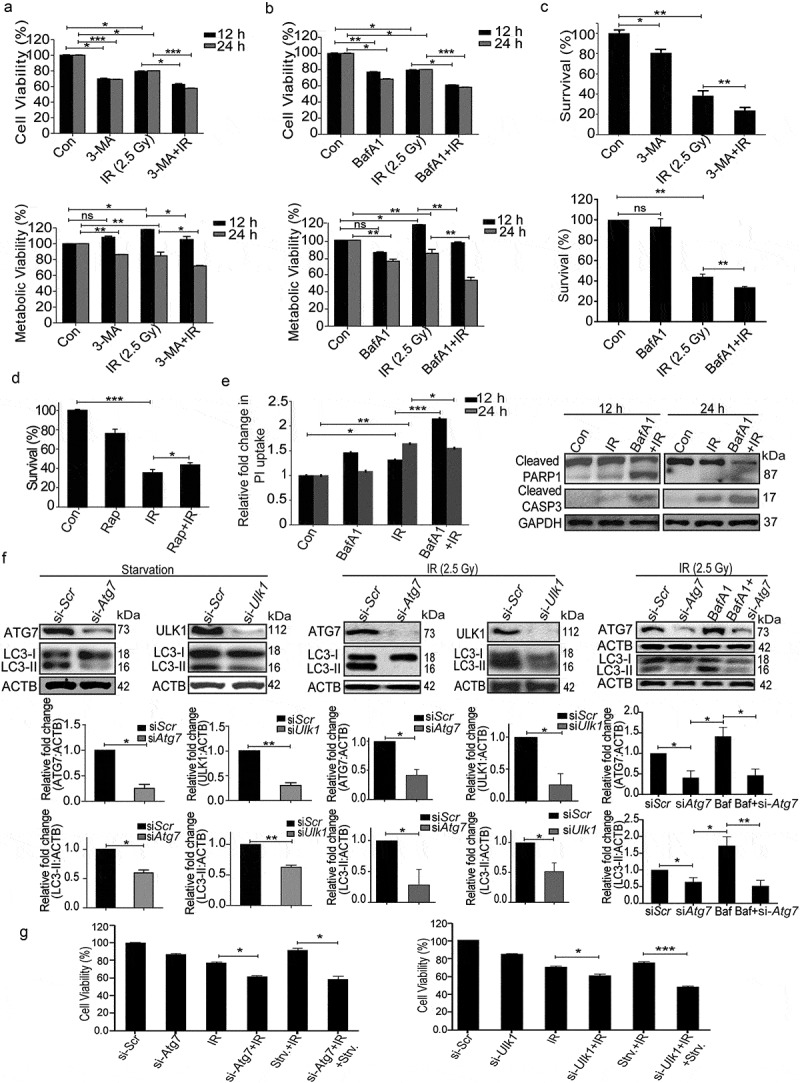
Radiation-induced autophagy is pro-survival and anti-apoptotic. (a) Cells were irradiated in the presence of the autophagy inhibitor, 3-MA (0.5 mM). SRB data (cell viability, shown in upper graph, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, at 12 and 24 h post-irradiation respectively) and MTT data (metabolic viability, shown in lower graph, *P < 0.05, at 12 and 24 h post-irradiation respectively) at 12 and 24 h post-irradiation shows the reduced viability of RAW 264.7 cells. (b) Cells were irradiated in the presence of the autophagy inhibitor, BafA1 (2.5 nM). Shown in the upper graph is cell viability (SRB) in the presence of BafA1 (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, at 12 and 24 h post-irradiation respectively) whereas in the lower graph, metabolic viability in the presence of BafA1 is shown (**P < 0.01, at 12 and 24 h post-irradiation respectively). (c) The clonogenic assay was performed to study the cell survival in the presence of 3-MA and BafA1. The bar graph shows the survival fraction of cells irradiated in the presence of 3-MA (upper panel) or BafA1 (lower panel). (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, for 3-MA+IR vs IR and BafA1+ IR vs IR, respectively). (d) Cell survival studies in the presence of the autophagy inducer rapamycin. The clonogenic assay was performed in the presence of 25 nM rapamycin. The bar graph shows the survival percentage of cells treated with rapamycin in the absence or presence of radiation. (e) Left panel: A bar graph showing mean fluorescence intensity of propidium iodide uptake in irradiated samples in the presence of BafA1 as compared to unirradiated control cells using flow cytometry at 12 and 24 h post-IR exposure. ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, at 12 and 24 h post-irradiation respectively. Right panel: Western blot analysis of cell lysate obtained at 12 and 24 h post-irradiation from BafA1+ IR treated cells. Blots were probed with intrinsic apoptosis markers, cleaved PARP1 and cleaved CASP3; GAPDH was used as a loading control. (f) Effect of Atg7 and Ulk1 siRNA on the levels of autophagy. Cells were reverse transfected with Atg7- and Ulk1-specific siRNAs (50 nM) and incubated for 24 h. Next, cells were either starved for 3 h or exposed to radiation, harvested after 24 h and immunoblotted with specific antibodies against ATG7, ULK1 and LC3. The effect of si-Atg7 on autophagic flux was further studied in the presence of BafA1. (g) Effect of genetic downregulation of autophagy on cell viability. Cells were reverse transfected with si-Atg7 and Ulk1 and incubated for 24 h. Next, cells were either starved for 3 h or kept in complete medium and exposed to 2.5 Gy radiation. After 24 h post-irradiation, SRB assay was performed to study cell viability. *P < 0.05, for IR vs si-Atg7, Strv.+IR vs si-Atg7+ IR+Strv., *P < 0.05 IR vs si-Ulk1+ IR and ***P < 0.001 Strv.+IR vs si-Ulk1+ IR+Strv. respectively. Strv., starvation.
