Figure 9.
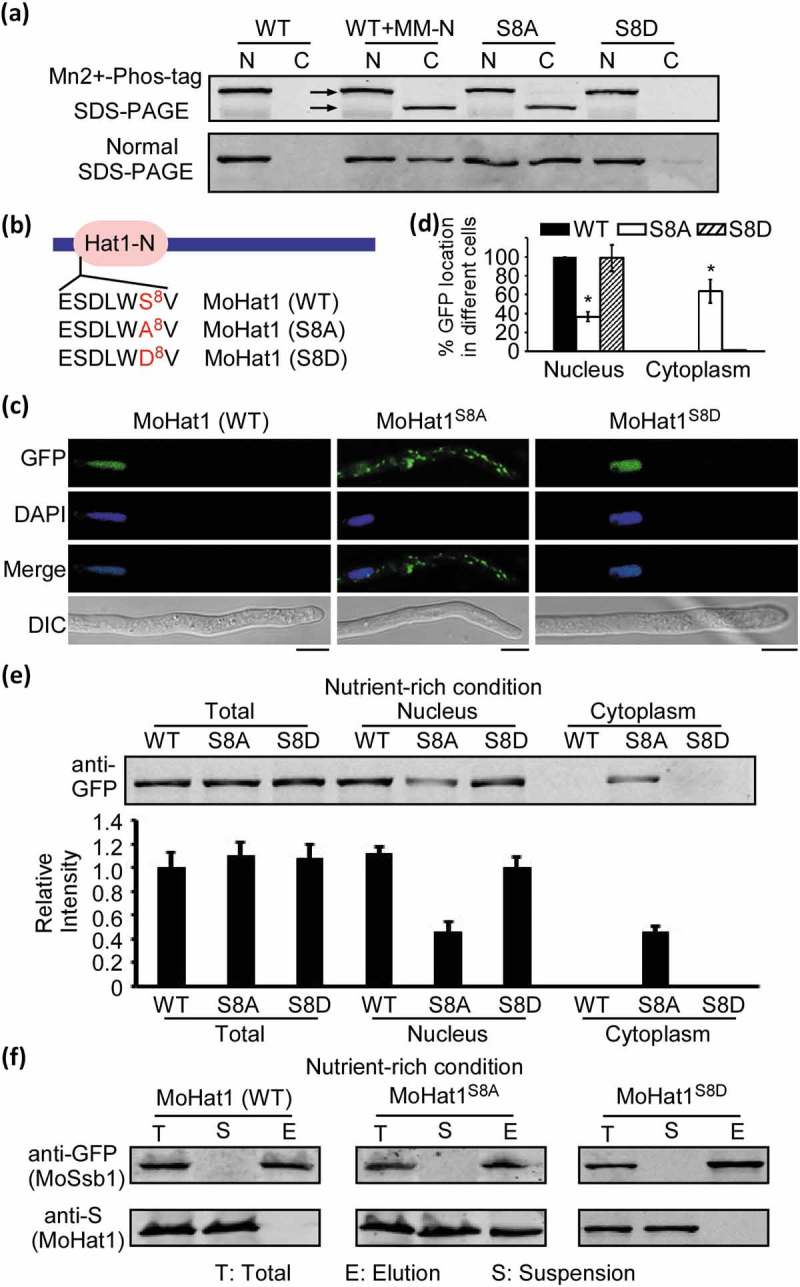
Phosphorylation of MoHat1 affects its subcellular localization. (a) Phosphorylation analysis of MoHat1. Nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins were extracted separately in the presence of phosphatase inhibitors and detected by Mn2+-Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and normal SDS-PAGE, respectively, and followed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody. S8A, constitutively unphosphorylated mutation; S8D, phosphomimetic mutation. (b) Phosphorylated peptides of MoHat1 identified by prediction and seriatim sites mutation. MoHat1 (S8A) and MoHat1 (S8D) indicate constitutively unphosphorylated and phosphomimetic mutation strain, respectively. (c) Localization of MoHat1 and its mutant strains (S8A and S8D) during nutrient-rich conditions. Scale bars: 5 μm. (d) Quantification of the percentage of GFP fluorescence signal localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm in ∆Mohat1/MoHAT1 (MoHat1 WT), ∆Mohat1/MoHAT1S8A (MoHat1S8A) and ∆Mohat1/MoHAT1S8D (MoHat1S8D) strains. Asterisks represent significant differences (Duncan’s new multiple range test, p < 0.01). (e) Western blot analysis of MoHat1 WT, S8A, and S8D mutant strains. Total, nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins were extracted separately using the Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction Kit and detected with the GFP antibody. The western blots were quantified with the ODYSSEY infrared imaging system (application software Version 2.1). Bars denote standard errors from 3 independent experiments. (f) Co-IP analysis for the MoHat1-MoSsb1 interaction in MoHat1 WT, S8A, and S8D mutant strains. Western blots of total proteins, suspensions and proteins eluted from anti-GFP agarose from transformants co-expressing MoSsb1-GFP and MoHat1-S, MoSsb1-GFP and MoHat1S8A-S, and MoSsb1-GFP and MoHat1S8D-S were detected with anti-S or anti-GFP antibodies, respectively. T, total; S, suspensions; E, elution.
