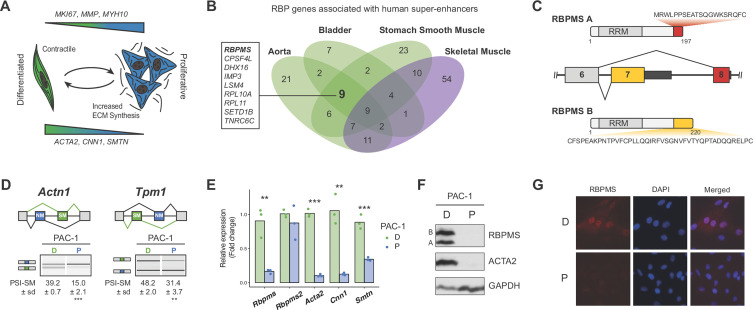
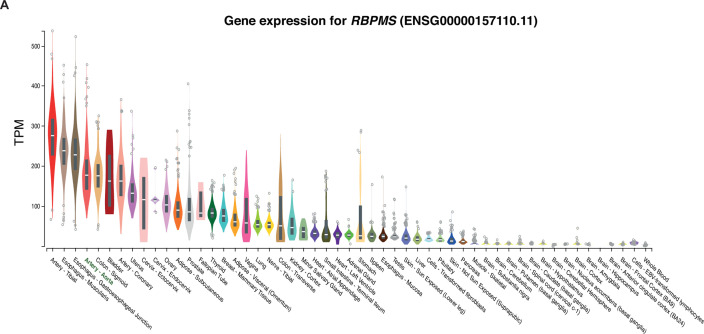
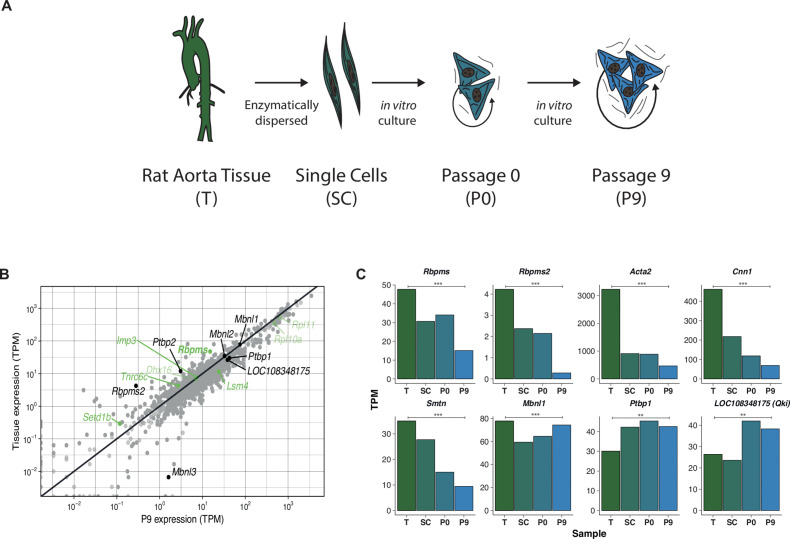
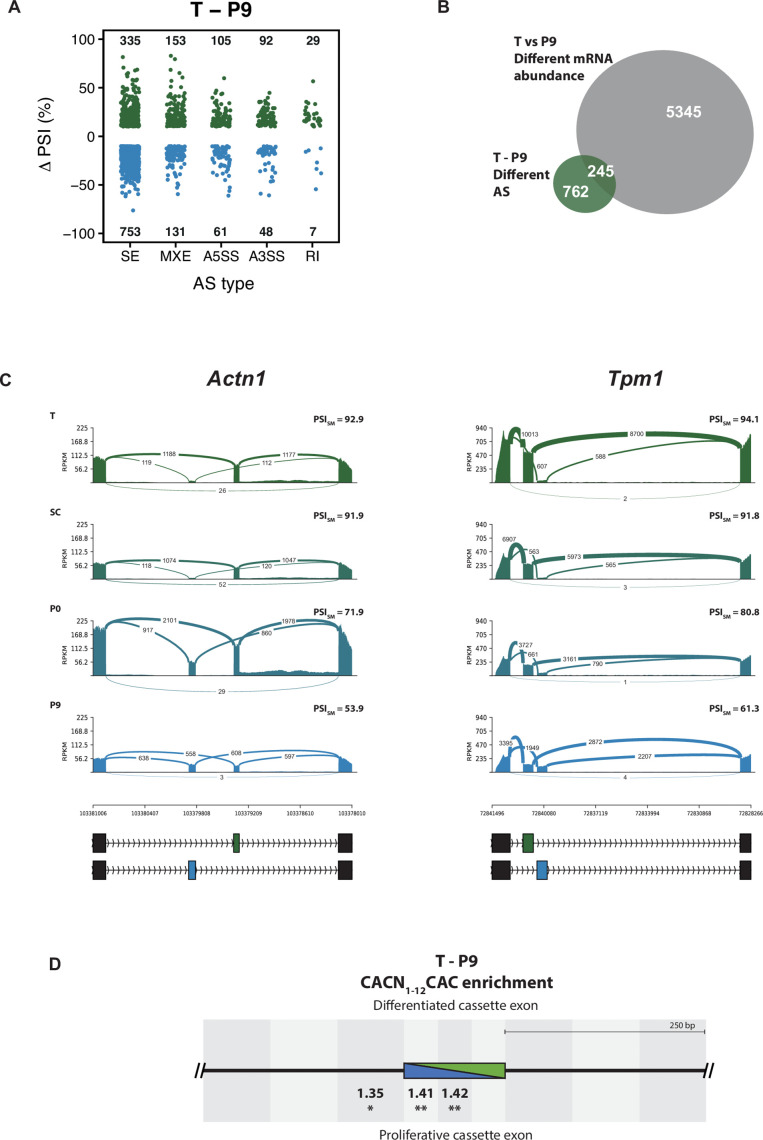
Figure 1. RBPMS is associated with SMC super-enhancers and is highly expressed in the differentiated PAC1 cells.
(A) Diagram of the SMC dedifferentiation. SMC markers of differentiation and dedifferentiation are respectively shown at the bottom and top of the diagram. (B) Venn diagram of RBP genes associated with super-enhancers across different human smooth muscle tissues. Skeletal muscle was used as an outlier. RBPs common to all smooth muscle tissues but not skeletal muscle are shown on the left. (C) Schematic of the AS event determining the two major RBPMS isoforms, RBPMS A (red) and RBPMS B (yellow). (D) RT-PCR analysis of SMC splicing markers, Actn1 and Tpm1, in differentiated (D) and proliferative (P) PAC1 cells. Schematic of the regulated mutually exclusive splicing events on top and respective isoforms products on the left. Values shown are the quantified PSI (percent spliced in) of the smooth muscle isoforms (SM) ± standard deviation (n = 3). (E) qRT-PCR analysis of Rbpms (all isoforms), Rbpms2 and SMC differentiation markers Acta2, Cnn1 and Smtn, in PAC1 cells D (green) and P (blue). Expression was normalized to the average of two housekeepers (Gapdh and Rpl32) and the mean of the relative expression is shown (n = 3). Each point shows data from an individual sample. Statistical significance was performed using Student’s t-test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). (F) Western blots for RBPMS in D and P PAC1 cells. ACTA2 is a SMC differentiation marker and GAPDH a loading control. A and B indicates the two RBPMS isoforms. (G) Immunofluorescence in D and P PAC1 cells for RBPMS. DAPI staining for nuclei.