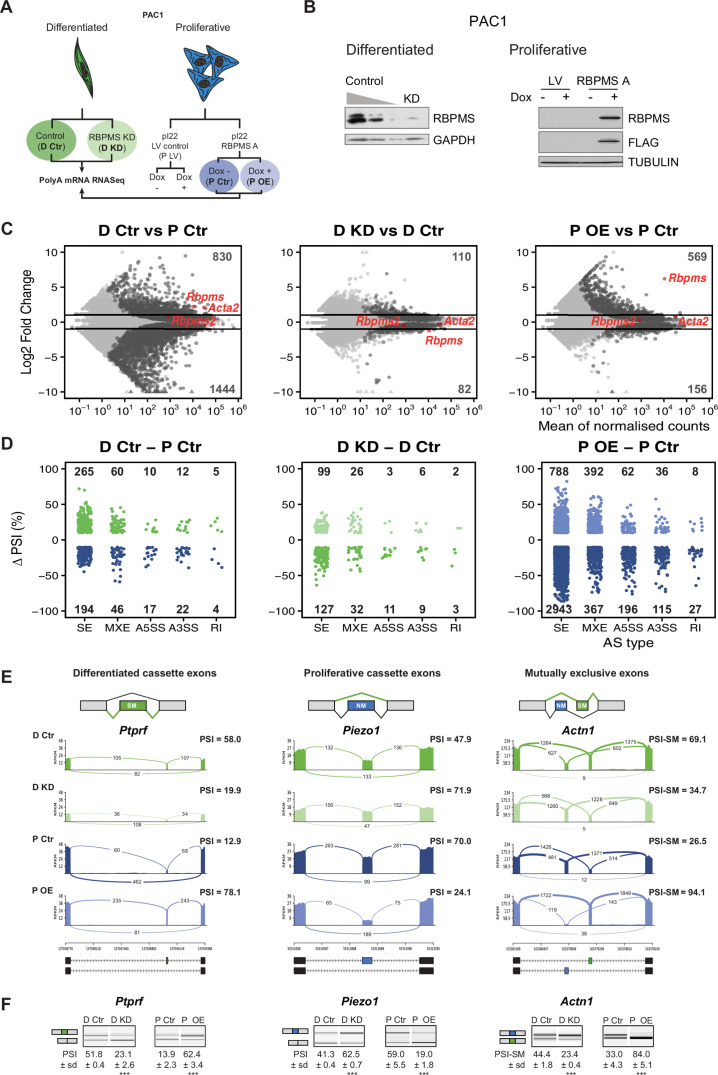
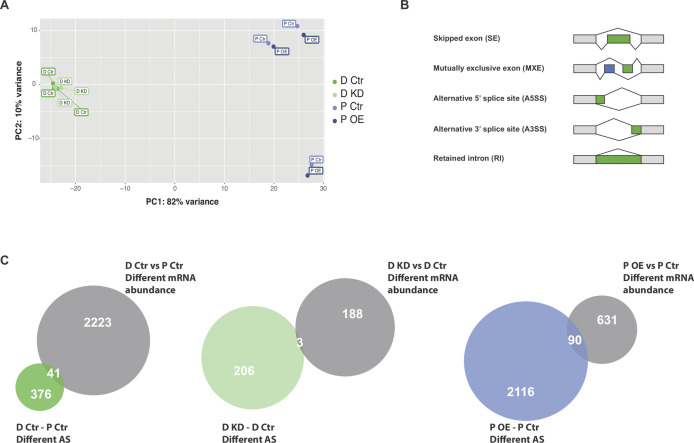
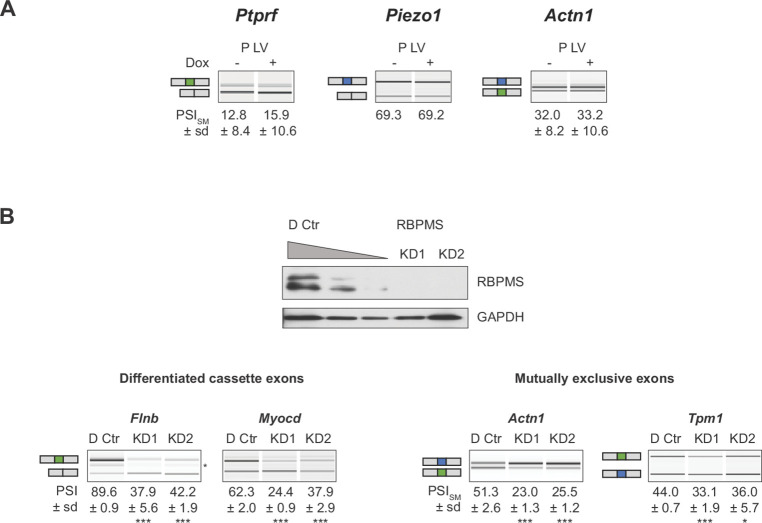
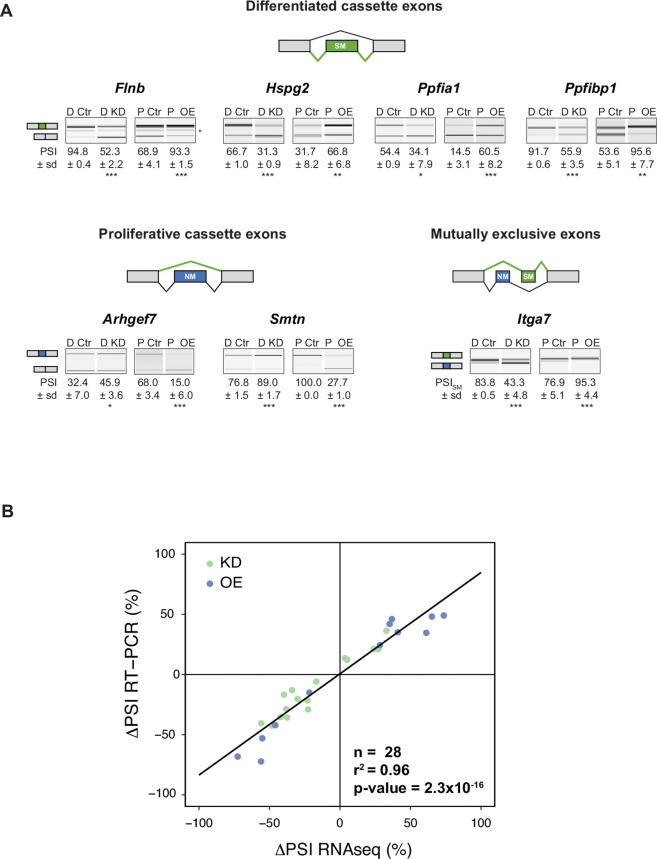
Figure 2. RBPMS regulates AS in PAC1 cells.
(A) Schematic of experimental design of RBPMS knockdown and overexpression in PAC1 cells. (B) Western blots for RBPMS in PAC1 knockdown, left, and inducible lentiviral overexpression, right. FLAG antibodies were also used for the overexpression of 3xFLAG tagged RBPMS. GAPDH and TUBULIN were used as loading controls. (C) MA plots of alterations in mRNA abundance in PAC1 dedifferentiation, left, RBPMS knockdown, middle, and RBPMS A overexpression, right. Dark gray: genes with significant changes (p-adj <0.05). Light gray: genes with p-adj ≥0.05. Red: Rbpms, Rbpms2 and the SMC marker, Acta2. Numbers of up and down-regulated are shown at top and bottom. Horizontal lines; log2 fold change = 1 and −1. (D) AS changes (FDR < 0.05 and ΔPSI greater than 10%) in PAC1 cell dedifferentiation, left, RBPMS knockdown, middle, and RBPMS A overexpression, right. ASE were classified into skipped exon (SE), mutually exclusive exon (MXE), alternative 5′ and 3′ splice site (A5SS and A3SS) and retained intron (RI) by rMATS. Numbers indicate the number of significant ASE of each event type between the conditions compared. (E) Sashimi plots of selected ASEs. Ptprf is shown as a differentiated cassette exon (green), Piezo1 as a proliferative cassette exons (blue) and Actn1 as a MXE. The numbers on the arches indicate the number of reads mapping to the exon-exon junctions. PSI values for the ASE are indicated for each condition. Values correspond to the mean PSI calculated by rMATS. In the case of the Actn1 MXE, the percent inclusion of the SM exon is shown (PSI-SM). Schematic of the mRNA isoforms generated by the alternative splicing are found at the bottom as well as the chromosome coordinates. (F) RT-PCR validation of ASEs from panel E. Values shown are the mean of the PSI ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using Student’s t-test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). See Figure 2—figure supplement 3 for more ASEs validated in the RBPMS knockdown and RBPMS A overexpression by RT-PCR.