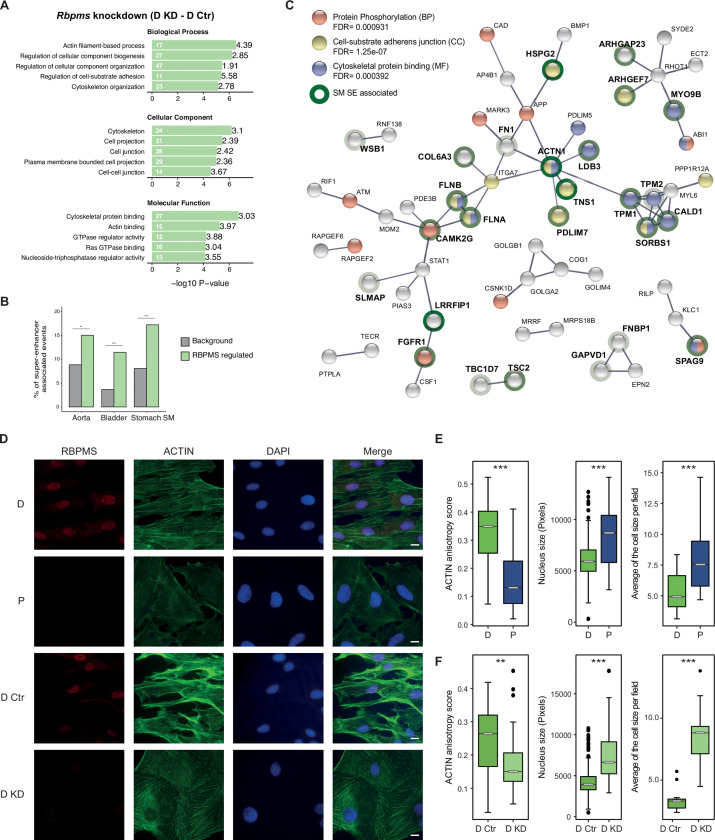
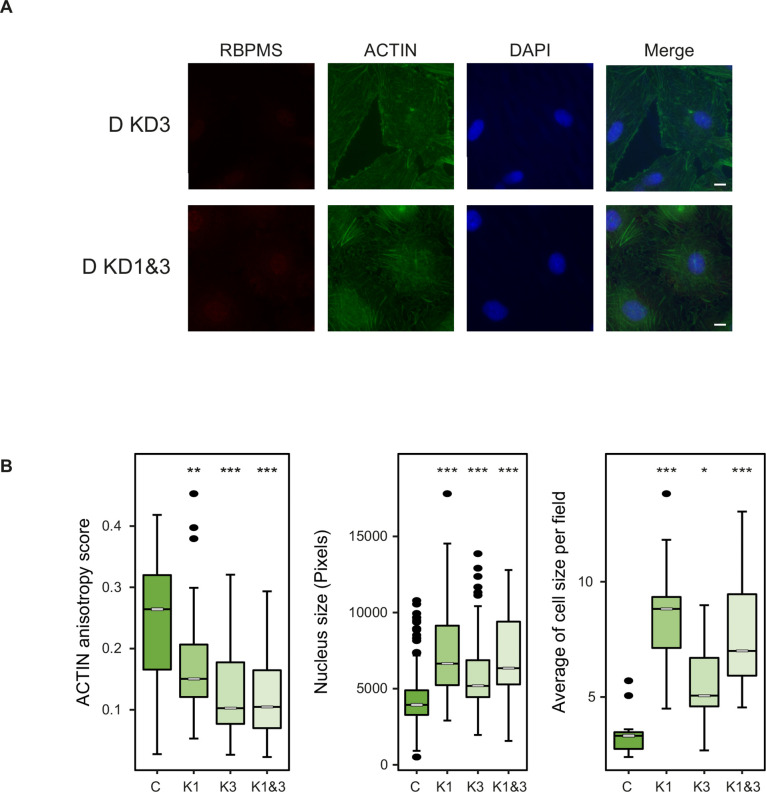
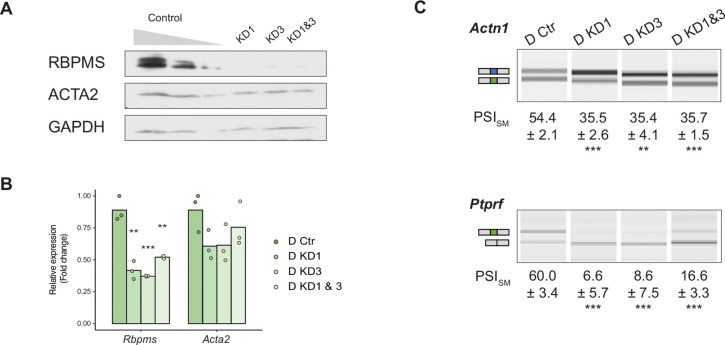
Figure 5. RBPMS regulates functionally important targets in SMCs.
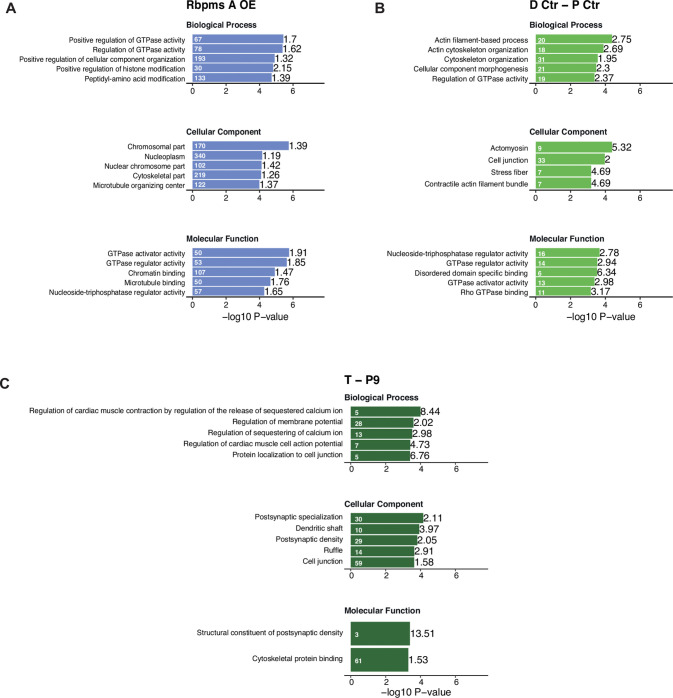
(A) GO analysis of genes with cassette exons regulated in RBPMS knockdown. The top five enriched GO terms in the three categories (biological process, molecular function and cellular component) are shown. Values within and in front of the bars indicate the number of genes in the enriched term and the enrichment relative to the background list. (B) Enrichment of exons regulated by RBPMS knockdown within genes associated with super-enhancers in smooth muscle tissues. Background set is all cassette exon events (regulated and unregulated) detected by rMATS in the same experiment. Significance determined by hypergeometic P-value. (C) PPI network of genes showing concordant splicing regulation upon RBPMS knockdown and PAC1 differentiation status, combined with genes concordantly regulated by RBPMS overexpression and in aorta tissue datasets. PPI network was generated in STRING using experiments and database as the sources of interactions. Network edges represent the interaction confidence. Enriched GO terms (BP, biological process, MF, molecular function and CC, cellular component) were also included in the analysis and are indicated in red, blue and yellow. Super-enhancer associated gene names are in bold and are highlighted gray, light green or dark green shading according to whether they were super-enhancer associated in 1, 2 or 3 SMC tissues. (D) Immunofluorescence of RBPMS and actin (Phalloidin) in differentiated and proliferative PAC1 cells (D and P) and upon prolonged (120 hr) RBPMS knockdown in differentiated PAC1 cells (D Ctr and D KD). DAPI staining for cell nuclei. Scale bars 10 μm. (E) Left, anisotropy measurement of actin fibers in PAC1 cells D (differentiated) and P (proliferative) using the FibrilTool ImageJ macro (n = 44 and 52). Middle, nucleus size measurement shown in pixels (n = 182 and 130). Right, average of the cell size quantified per field (n = 11 and 15). (F) Left, anisotropy measurement of actin fibers in RBPMS knockdown (D Ctr and D KD) using the FibrilTool ImageJ macro (n = 56 and 33). Middle, nucleus size measurement shown in pixels (n = 363 and 75). Right, average of the cell size quantified per field (n = 14 and 10). In (E) and (F), statistical significance was obtained from a Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon Test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Data shown are from one representative experiment carried out in triplicate.