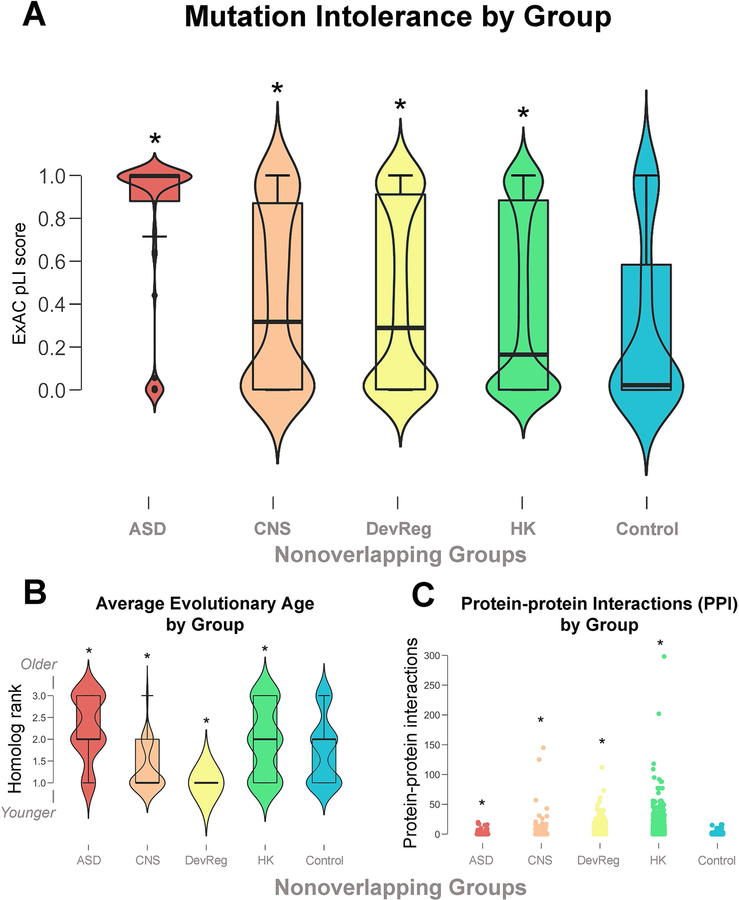
Figure 2.
(A) ExAC pLI scores across non-overlapping groups. Higher pLI scores indicate greater sensitivity to loss-of-function mutations. All gene groups, including controls, exhibit an hourglass formation suggesting genes tend to be either very mutation tolerant or intolerant with fewer genes falling intermediate. (B) Average evolutionary age across non-overlapping groups. Both autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and housekeeping (HK) genes appear to be significantly older than central nervous system (CNS) genes, developmental regulatory (DevReg) genes, and controls. (C) Number of protein-protein interactions (PPI) according to non-overlapping groups. All experimental gene groups significantly differed from size- and ExAC pLI-matched controls as indicated with an asterisk.