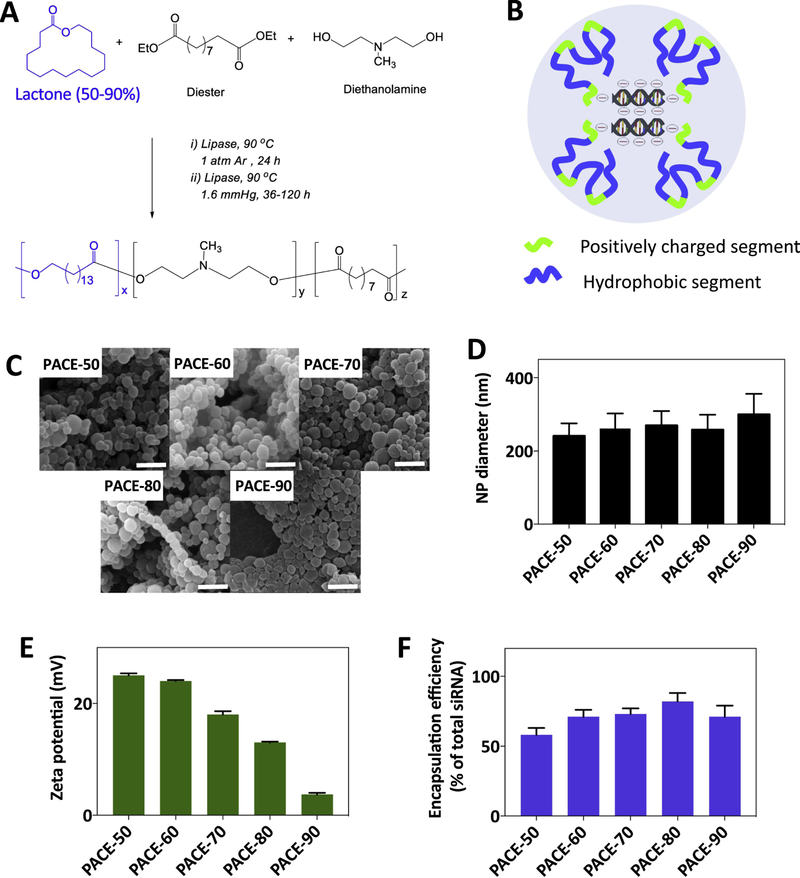
Figure 1. Characterization of siRNA-loaded PACE NPs.
(A) PACE polymers were synthesized by enzyme-catalyzed copolymerization of 15-pentadecanolide (PDL), diethyl sebacate (DES) and N-methyldiethanolamine (MDEA), as described previously [18]. (B) Cationic amines on PACE NPs condense siRNA molecules into the core of NPs and also facilitate NP uptake into cells. (C,D) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of siRNA-loaded PACE NPs synthesized with 50% to 90% PDL. NP diameter was quantified using image J. Scale bar: 1 μm. (E) NP zeta potential was measured using a Zetasizer (Malvern Instruments). (F) NPs were dissolved in methylene chloride for 2 hours. siRNA was extracted into Tris-EDTA buffer and siRNA was quantified using QuantIT PicoGreen assay (Invitrogen). The siRNA amount for all formulations was 500 pmol siRNA/mg of polymer, and encapsulation efficiency was calculated as: encapsulated siRNA/total feed siRNA x 100%. In panels D, E, and F, n = 4 for all formulations.