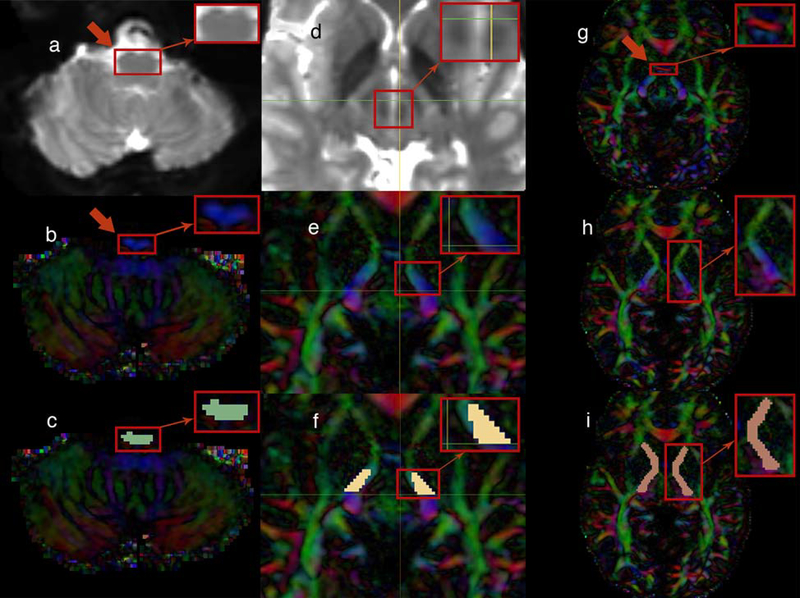
Fig. 1.
(left portion) The upper medulla oblongata, rostral to the inferior olivary nucleus, was located in the baseline (b0) MRI brain images (axial plane) as indicated by the arrow (a). The same area is illustrated in diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) (axial plane) as indicated by the arrow (b). Finally, the medulla-region-of-interest (medulla-ROI) was drawn to the targeted region (axial plane) (c)
(middle portion) The region included in the square was located in the baseline (b0) MRI brain images in order to detect the red nucleus (axial plane) (d). The region of the cerebral peduncle of the brainstem rostral to the substantia nigra and red nucleus (thereby, rostral to the horizontal level marked by the green line in the image) was targeted (axial plane) (e). Finally, the brainstem-ROI was drawn to that area (axial plane) (f)
(right portion) The anterior commissure (AC) level was located as indicated by the red color-coded fibers that disappear in the next image (axial plane) (see the red arrow) (g). Just after the AC was no longer visualized in the DTI and moving superiorly, the internal capsule (IC) was targeted as illustrated (axial plane) (h). Therefore, the capsular-ROI was drawn to the IC at the level of the AC (axial plane) (i)