Fig. 1. Signaling pathways triggered by the cell surface receptors for S1P (S1PRs) and C1P (C1PR).
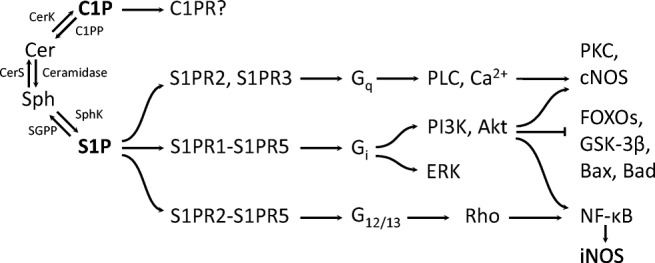
S1P through its G protein-binding receptors modulates pathways known for their engagement in the regulation of cellular metabolism oxidative/nitrosative stress and death/survival. The depicted examples of S1PR-activated signaling pathways are far from exhausting the spectrum of observed interactions (e.g., S1PR2 inhibits Akt while S1PR3 activates it; iNOS is typically induced by NF-κB, but can also undergo S1P-/C1P-dependent suppression via p38 MAPK [8, 33]). In contrast, C1PR, the cell surface receptor for ceramide-1-phosphate, remains poorly characterized and it is generally not known what part of C1P effects it mediates. According to [34], modified
