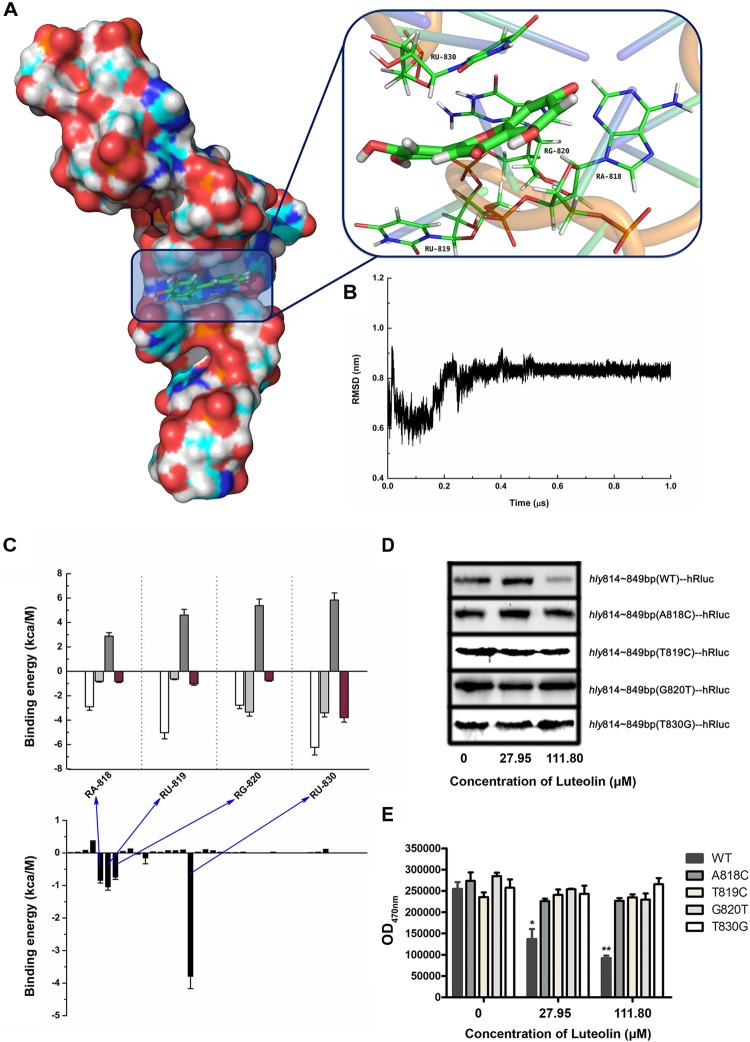
FIGURE 3.
Molecular modeling of the binding mechanisms of luteolin to hly mRNA. (A,B) The binding mode of luteolin to mRNA based on MD simulation. The 3D structure and the bases in the binding site in the complex (A) and the RMSD of the backbone atoms of the mRNA with luteolin (B). (C) Decomposition of the binding energy per base in the binding site of the mRNA-luteolin complex. A818, U819, G820, and U830 had the strongest interaction with luteolin. (D) The effect of luteolin on the production of recombinant luciferase with the hly sequence (nt 814–849) or a mutant version. The luciferase reporter gene with the wild-type (nt 814–849) or mutant hly sequence was cloned into pET21a+, and the recombinant protein was synthesized as described above. (E) The luciferase activity in the samples containing the wild-type (nt 814–849) or mutant hly sequence was measured using the Renilla luciferase assay system. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01.