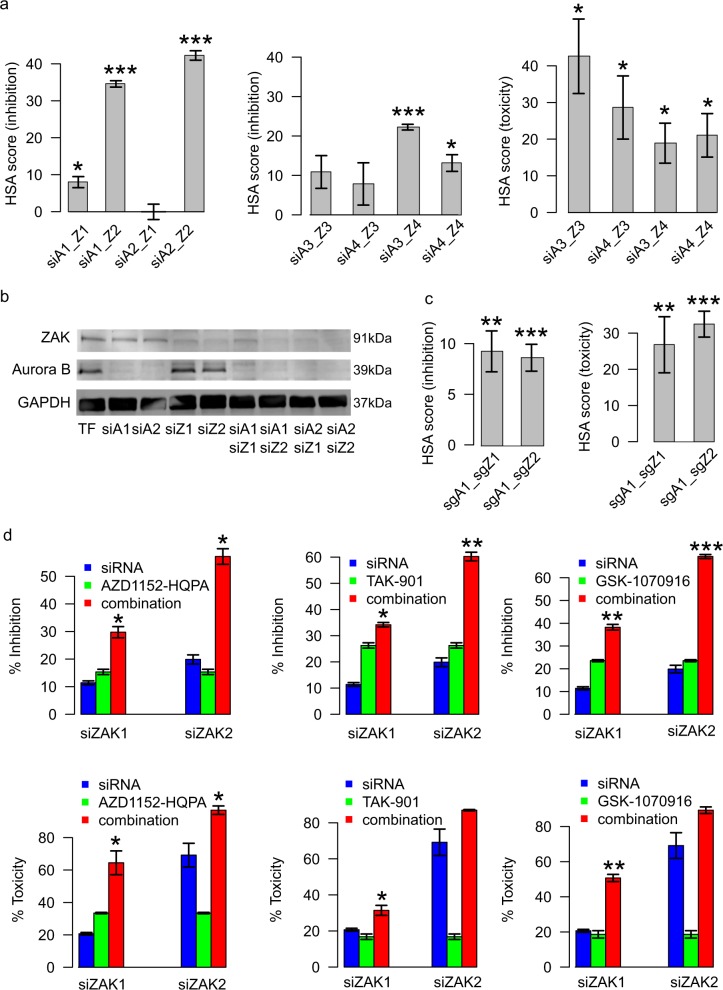
Fig. 3.
Experimental confirmation of the Aurora B and ZAK interactions in MDA-MB-231. a Validation of the AURKB–ZAK interactions using two Qiagen siRNAs (siA1 and siA2) and two Ambion siRNAs (siA3 and siA4) for AURKB, and similarly for ZAK (siZ1–siZ4). For each siRNA, 16 nM of final concentrations were used for both single siRNAs and double siRNAs (i.e., an 8+8 nM combination in double siRNAs). The highest single agent (HSA) synergy scores were calculated as the difference between the siRNA double knockdown effects minus the maximal effects of the single knockdowns in cell viability inhibition (CellTiter-Glo) and toxicity (CellTox Green) assays, respectively (see Methods for details). Standard error of means was calculated over three replicates. b Knockdown effect of AURKB and ZAK by each of the individual Qiagen siRNAs and their combinations using Western blot assays. Standard error of means was calculated over three replicates. c HSA synergy scores for AURKB and ZAK double knock-out using combinatorial sgRNAs (sgA1 for AURKB and sgZ1, sgZ2 for ZAK) in CRISPR/Cas9 system. Standard error of means was calculated over eight replicates. d Cell inhibition and toxicity effects were measured for Aurora B inhibitors combined with the two ZAK siRNAs. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (Wilcoxon rank sum test, two-sided). The labels on the x-axis indicate the different siRNA combinations