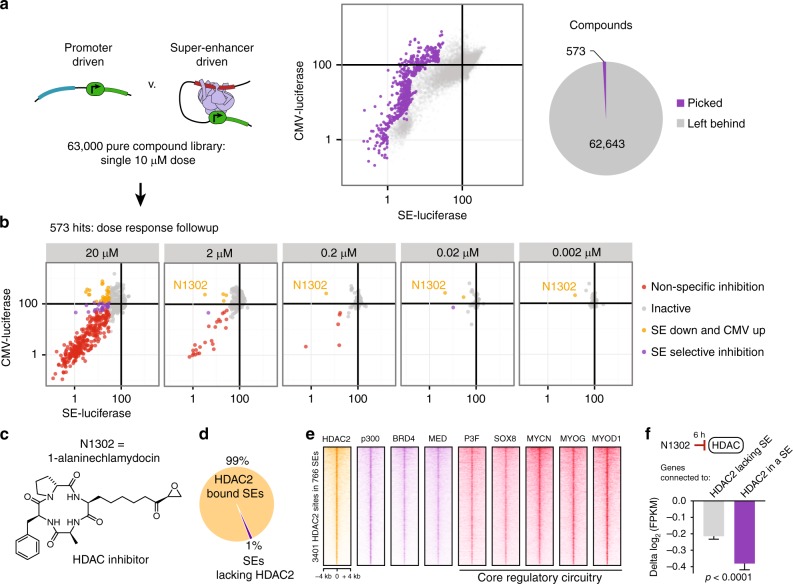
Fig. 2.
HDAC is a key chemical vulnerability core regulatory TF-driven transcription. a First pass screening of 63,000 pure compounds against constitutive promoter-driven (CMV) and SE-driven luciferase. Assay was performed after 24 h of 10 µM exposure to each drug in duplicate. 573 of the most selective small molecules were chosen for follow-up screening. b Validation of 573 hits by dose–response screening identified the molecules that continued to perform as SE-selective transcriptional inhibitors at lower doses, most notably compound N1302. Points represent the mean of four technical replicates. c Structure of N1302, 1-alaninechlamydocin, an epoxide-containing cyclic tetrapeptide known to potently inhibit histone deacetylases. d HDAC2 occupies virtually all super enhancers. Pie chart depicts super enhancers in RH4 cells either bound (99%) or unbound (1%) by HDAC2 assessed by overlap of high-confidence (q < 10−9) ChIP-seq peaks. e HDAC2 sites (n = 3401) in SEs (n = 766) are co-bound by enzymatically opposing HAT (p300), BRD4, mediator, and core regulatory TFs. ChIP-seq signal is plotted as heatmaps of 8 kb surrounding each HDAC2 peak, as detected in FP-RMS (RH4 cells). f HDAC inhibitor has selective transcriptional impact on SE-associated, HDAC2 proximal genes. N1302 was dosed in RH4 cells for 6 h at 1 µM. Error bars represent 95% confidence interval; P-value was calculated by Welch’s unpaired t-test