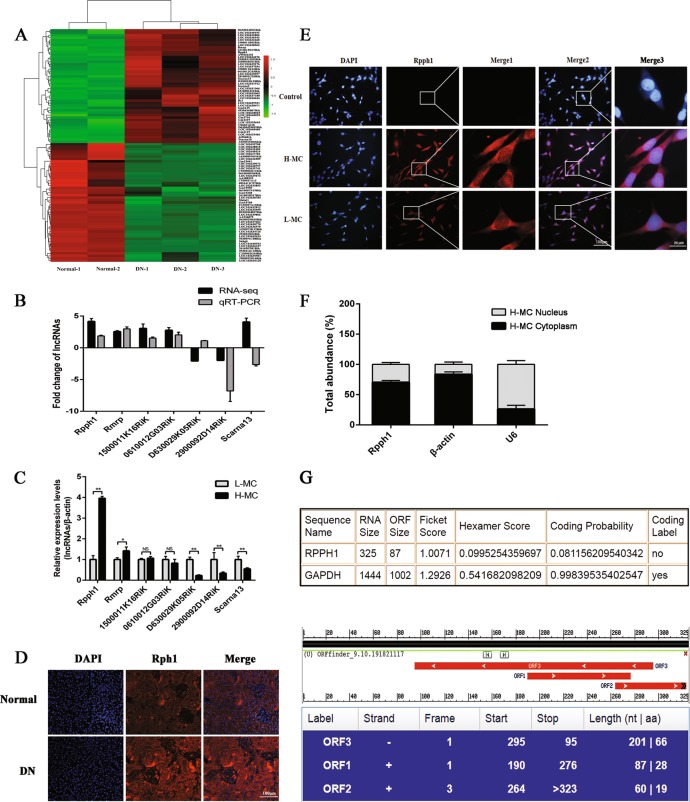
Fig. 1. Increased expression of Rpph1 (ribonuclease P RNA component H1) was observed in diabetic nephropathy (DN) both in vivo and in vitro.
a Dysexpressed long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were examined in the renal tissue of db/db DN mice (n = 3 for 12 weeks) and normal controls (n = 2 for 12 weeks) by RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) (q < 0.05). b Comparison of the expression of seven putative lncRNAs identified by RNA-seq and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The samples for qRT-PCR were the renal tissues of db/db DN mice (n = 3 for 12 weeks) and normal controls (n = 3 for 12 weeks); the data are representative of three independent experiments. c The seven putative lncRNA candidates were detected by qRT-PCR in mesangial cells (MCs) cultured under low (5.5 mmol/L glucose) or high glucose (25 mmol/L glucose) conditions; the data are representative of three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, NS no significant difference. d Rpph1 exhibited higher expression in the renal tissue of db/db DN mice (n = 3 for 12 weeks) than in the normal group of mice (n = 3 for 12 weeks) as identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). The data are representative of three independent experiments. e Rpph1 (Red) was mainly distributed in the cytoplasm of MCs cultured under low (5.5 mmol/L glucose) or high glucose (25 mmol/L glucose) conditions, as identified by FISH (×400). Merge 1: the enlarged cutouts without 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI); Merge 3: the enlarged cutouts with DAPI. f Rpph1 was mainly observed in the cytoplasm of MCs cultured under high glucose (25 mmol/L glucose) conditions by qRT-PCR; β-actin was the cytoplasm control and U6 was the nucleus control. The data are representative of three independent experiments. g The protein-coding ability of Rpph1 was predicted by bioinformatics methods. Upper: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool (CPAT) was used to test the protein-coding ability of Rpph1. Lower: ORF finder was used to analyze the protein-coding ability of Rpph1