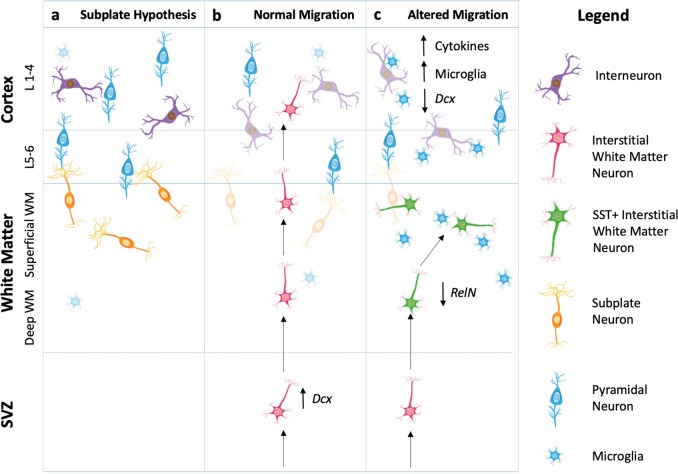
Fig. 1.
Hypothetical mechanisms for the role of interstitial white matter neurons (IWMNs) in normal and schizophrenia-related brains. a IWMNs may represent remaining subplate neurons that form connections with cortical pyramidal neurons in layers 5-6 of the overlying cortex. b IWMNs may be part of a normal restorative brain mechanism, migrating to the cortex in response to particular brain cues. The type of IWMN that responds depends on the brain cue. c In schizophrenia, cortical inflammation causes damage to particular neurons (e.g., SST+ interneurons) which may trigger neurogenesis but these SST+ IWMNs fail to migrate radially and terminate in the white matter from early in development