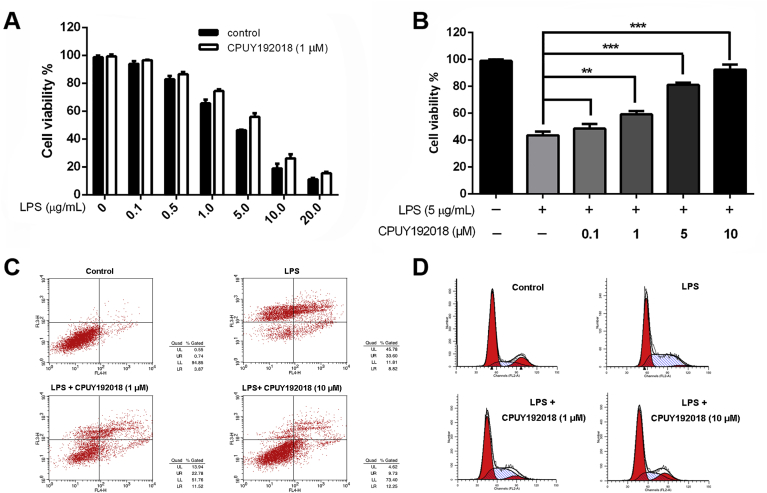
Fig. 4.
Effects of CPUY192018 on the LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells. (A) Protective effects of CPUY192018 against LPS-induced cell damage. HK-2 cells were pretreated with 1 μM CPUY192018 for 10 h then exposed to various concentrations of LPS for an additional 12 h. Cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. The values shown are the means ± SEM (n = 3 independent observations). (B) Concentration-dependent protective effects of CPUY192018 against the LPS-induced cell damage. HK-2 cells were pretreated with 0.1–10 μM CPUY192018 for 10 h then exposed to 5 μg/mL LPS for an additional 12 h. The cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. The values shown are the means ± SEM (n = 3 independent observations). (C) Flow cytometry analysis of the apoptotic rate. HK-2 cells were treated with CPUY192018 for 10 h before being exposed to 5 μg/mL LPS for an additional 8 h. The apoptotic rates were detected by flow cytometry. The statistical analysis of the apoptotic rates is shown in figure. (D) The effect of CPUY192018 on the cell cycle in HK-2 cells. HK-2 cells were treated with CPUY192018 for 10 h before being exposed to 5 μg/mL LPS for an additional 8 h. The effects of CPUY192018 on the cell cycle in HK-2 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The statistical analysis of the ratio of HK-2 cells in the G0/G1, S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle are shown in the figure.