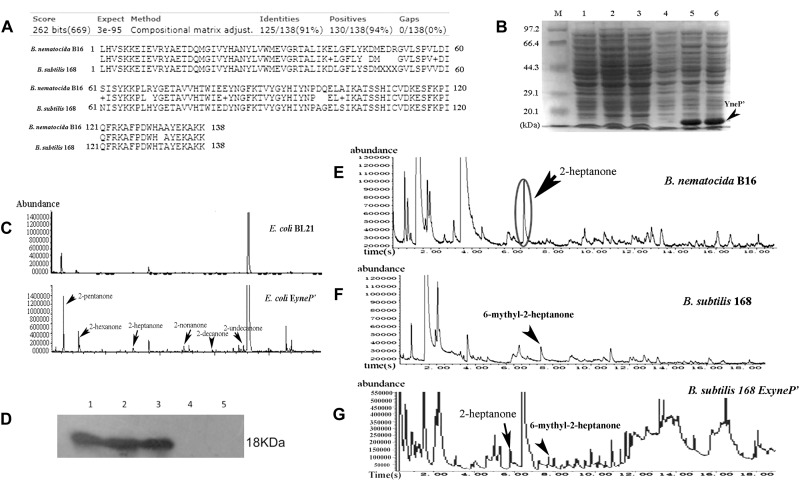
FIGURE 5.
The yneP’ gene in the non-pathogenic B. subtilis 168 has the methylketone synthetase activity but absence of 2-heptanone in the VOCs from B. subtilis 168. (A) The YneP’ in B. subtilis 168 showed highly homologous to YneP in B. nematocida B16. (B) SDS-PAGE confirmed expression of the recombinant protein of YneP’ in E. coli BL21. Lane M, the protein Marker; lane 1 and 2, the negative control of E. coli BL21 with blank vector; lane 3 and 4, the strain E. coli BL21 with ExyneP’ without IPTG induction; lane 5 and 6, the heterologous expression of YneP’ in E. coli BL21 after induced with 0.1 mM IPTG. The molecular size of target protein is about 18 kDa. (C) GC-MS analyses of the VOCs from E.coli ExyneP’ and the negative control. (D) Western blot to the homolously expressed YneP’ with 6 × his tag using anti-his antibody. Lane 1–3 represented the three positive transformants of B. subtilis 168 ExyneP’; Lane 4 and 5 represented the wild type B. subtilis 168 and B. subtilis 168 with the blank vector pDG148. (E–G) Comparisons of the VOCs among B. nematocida B16, B. subtilis 168, and B. subtilis ExyneP’. Among those three strains, the peak of 2-heptanone was detected in B. nematocida B16 but absence in B. subtilis 168. Instead, a peak of 6-methyl-2-heptanone could be detected in B. subtilis 168. But 2-heptanone in VOCs reappeared when overexpressing yneP’ in B. subtilis 168.