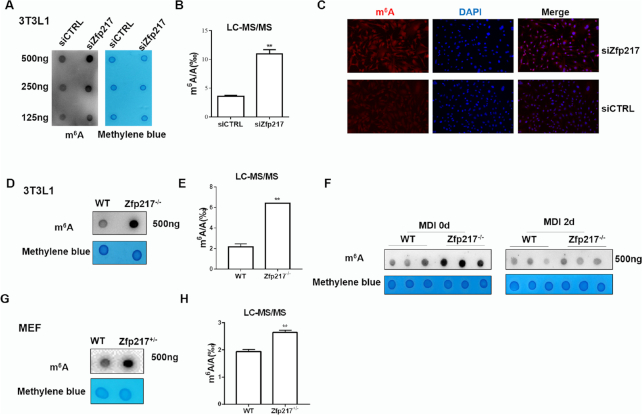
Figure 2.
Zfp217 depletion increases m6A modification in 3T3L1 cells. (A) Dot blot was used to detect the m6A modification after knockdown of Zfp217. Methylene blue staining was used as a loading control (n = 3). (B) m6A/A ratio in polyadenylated RNA was measured from control and Zfp217 knockdown 3T3L1 cells using LC-MS/MS (n = 2). (C) m6A immunostaining of 3T3L1 cells transfected with siCtrl and siZfp217. Nucleus was stained with DAPI (magnification: 200×). (D) Dot blot was used to detect the m6A modification after knockout of Zfp217 (n = 3). (E) m6A modification levels were measured after knockout of Zfp217 using LC-MS/MS (n = 2). (F) m6A level during adipogenesis of 3T3L1 (n = 3). (G) Dot blot was used to detect the m6A modification in MEF-Zfp217+/- cells (n = 3). (H) m6A modification level was measured in MEF-Zfp217+/− cells using LC-MS/MS (n = 2). Presented as means ± SD (**P < 0.01).